The Classical Complement Cascade Mediates CNS Synapse Elimination
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 25 fevereiro 2025

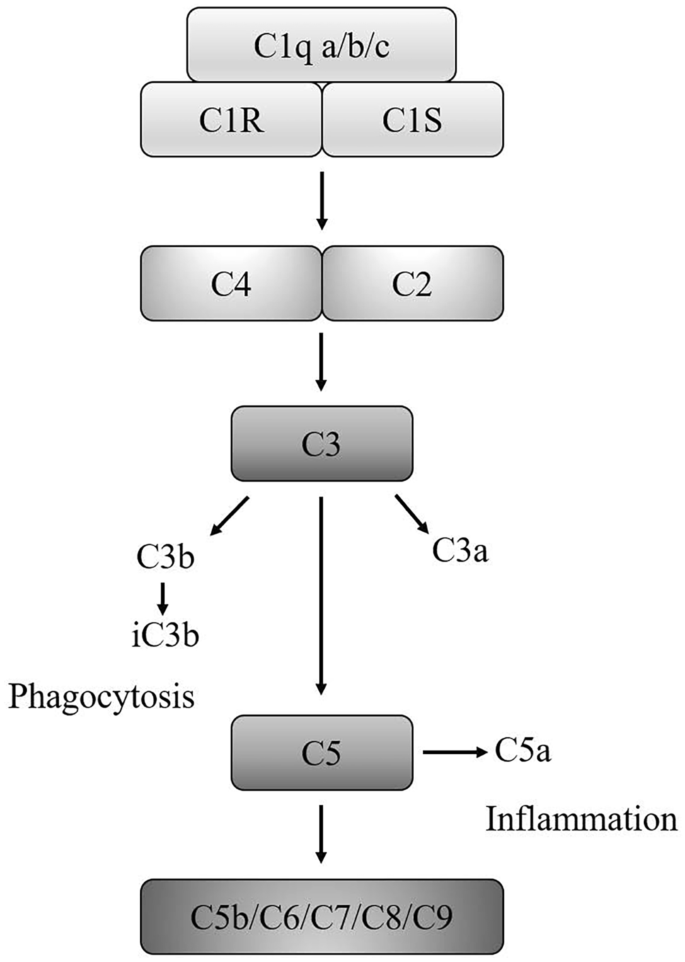
As a Potential Therapeutic Target, C1q Induces Synapse Loss Via Inflammasome-activating Apoptotic and Mitochondria Impairment Mechanisms in Alzheimer's Disease

Full article: The case for complement component 5 as a target in neurodegenerative disease
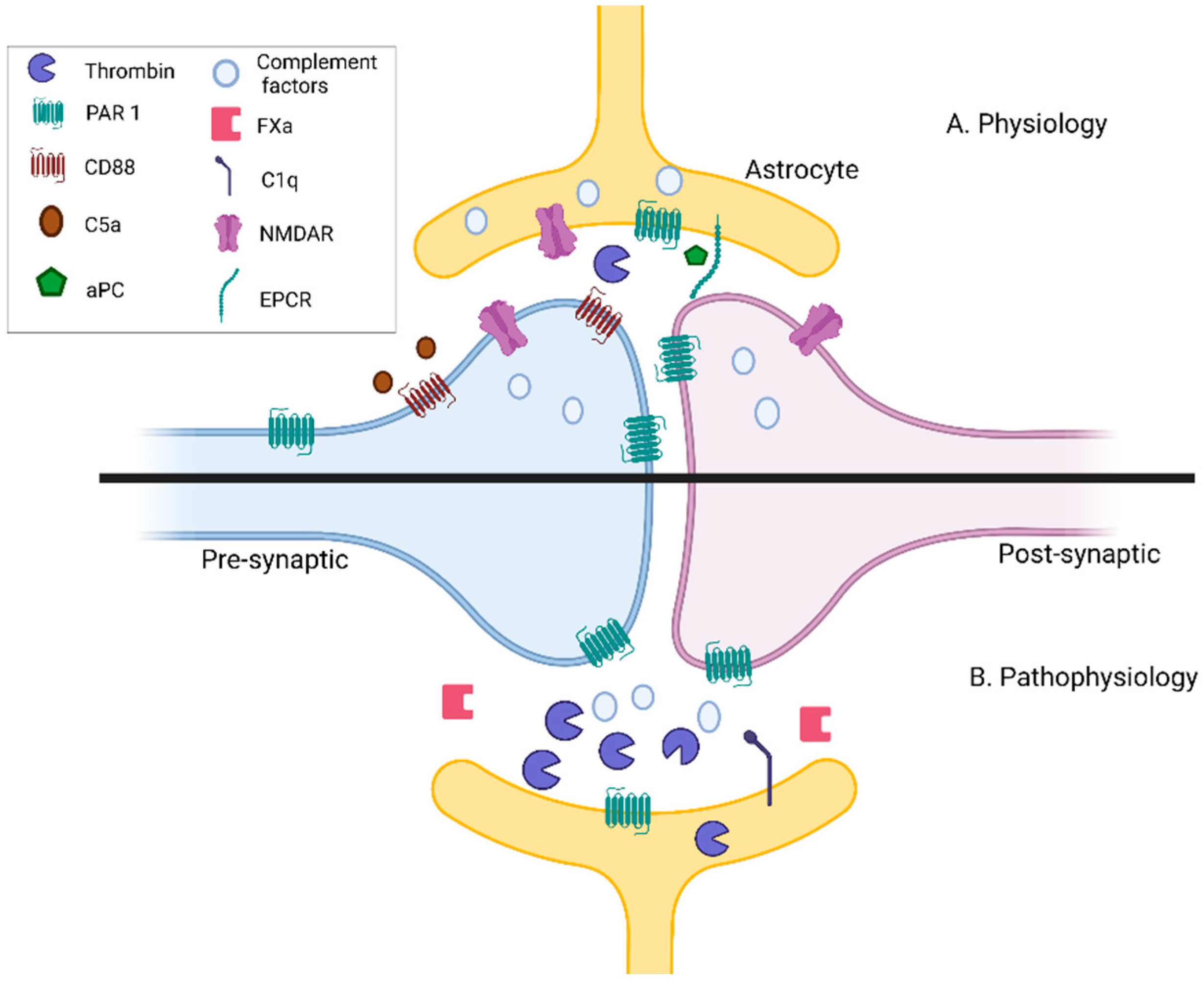
Biomedicines, Free Full-Text
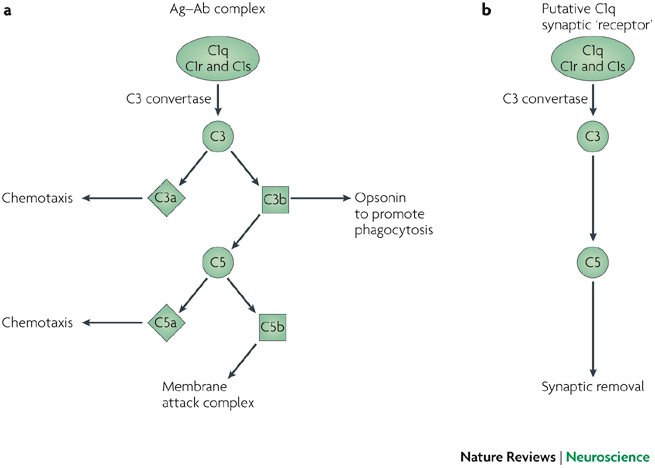
C1q: the perfect complement for a synaptic feast?

Glia, Neurobiology Journal
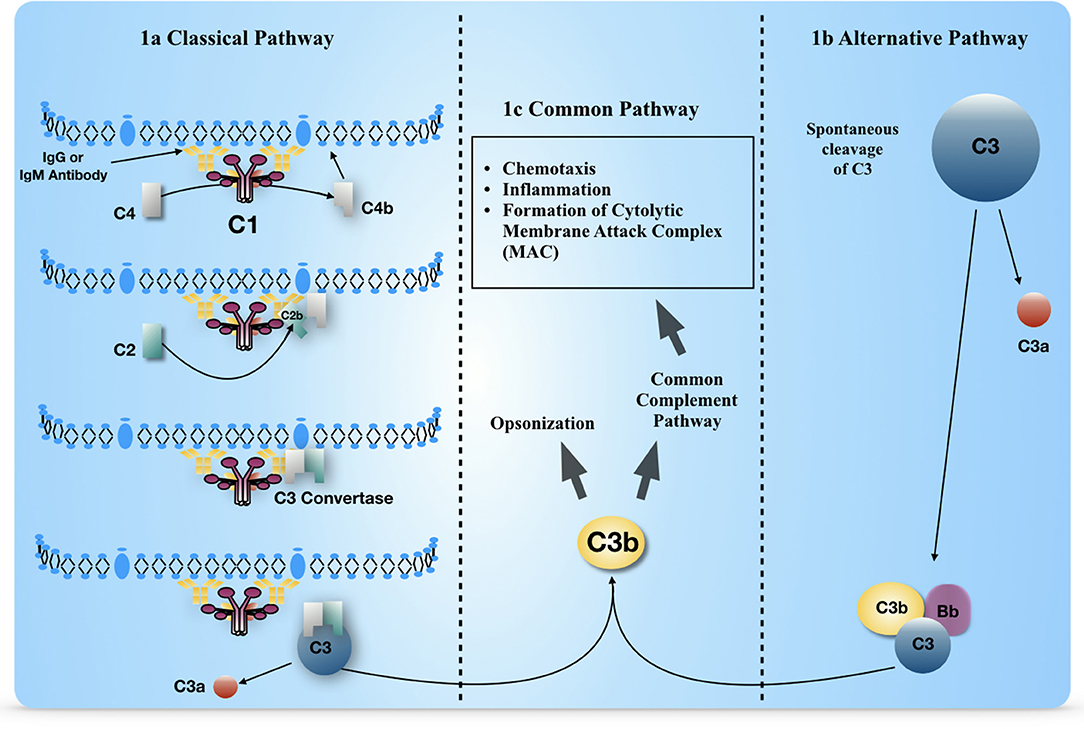
Frontiers Complement Activation in the Central Nervous System: A Biophysical Model for Immune Dysregulation in the Disease State

Microglial trogocytosis and the complement system regulate axonal pruning in vivo

Complement C3-dependent glutamatergic synapse elimination in the developing hippocampus is region- and synapse-specific

The Classical Complement Cascade Mediates CNS Synapse Elimination: Cell

Figure 2 from The complement system: an unexpected role in synaptic pruning during development and disease.

A new age for (mucosal) NeuroImmunology - Mucosal Immunology

Complement and microglia mediate early synapse loss in Alzheimer mouse models
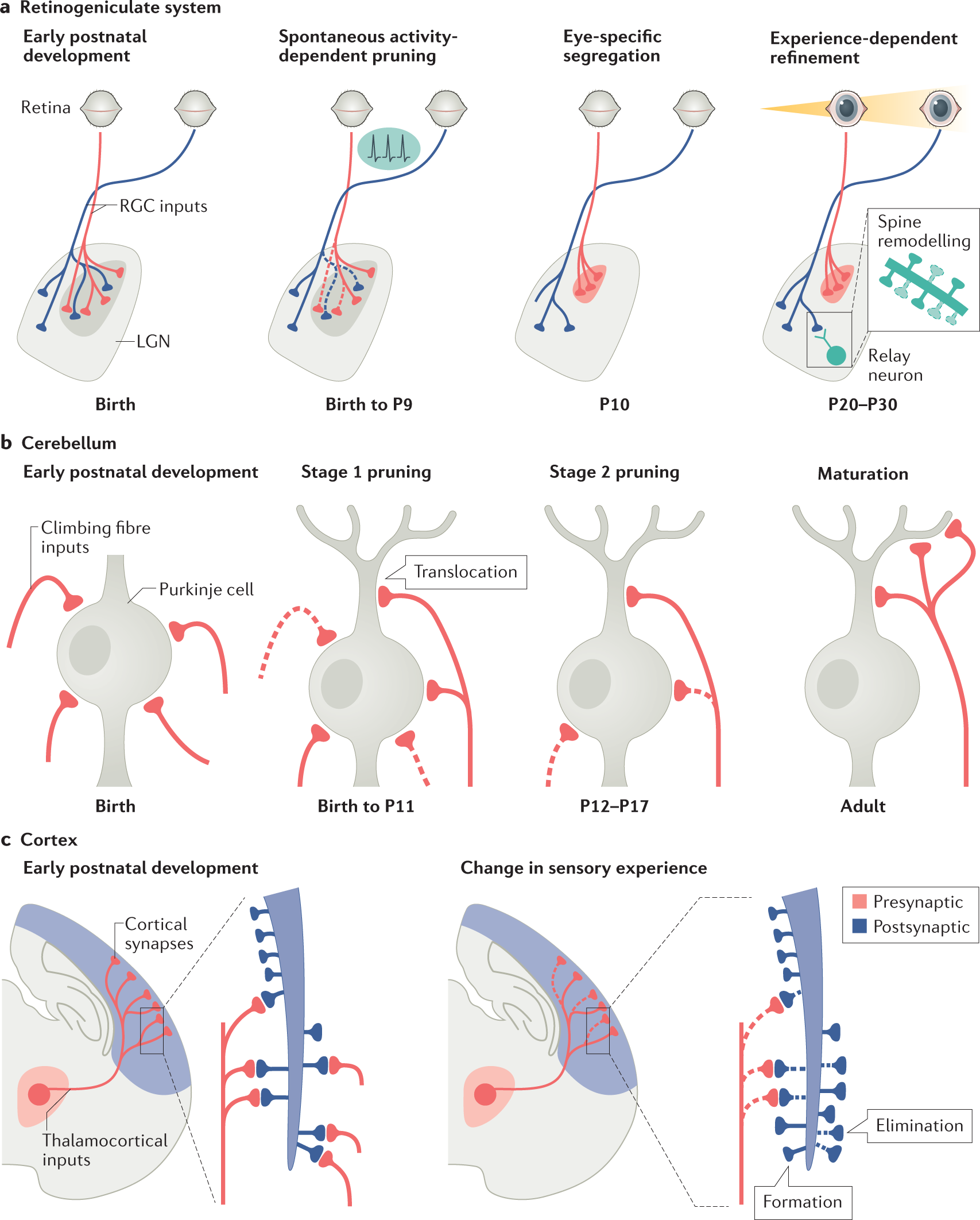
Mechanisms governing activity-dependent synaptic pruning in the developing mammalian CNS
Recomendado para você
-
synapse-x-2023 · GitHub Topics · GitHub25 fevereiro 2025
-
synapse-x-free · GitHub Topics · GitHub25 fevereiro 2025
-
2023 Synapse x failed to download launcher data research This25 fevereiro 2025
-
 Synapse X Join Anyone Download - Colaboratory25 fevereiro 2025
Synapse X Join Anyone Download - Colaboratory25 fevereiro 2025 -
Spaceborne data analysis with Azure Synapse Analytics - Azure Architecture Center25 fevereiro 2025
-
 A Versatile Synthetic Affinity Probe Reveals Inhibitory Synapse Ultrastructure and Brain Connectivity** - Khayenko - 2022 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley Online Library25 fevereiro 2025
A Versatile Synthetic Affinity Probe Reveals Inhibitory Synapse Ultrastructure and Brain Connectivity** - Khayenko - 2022 - Angewandte Chemie International Edition - Wiley Online Library25 fevereiro 2025 -
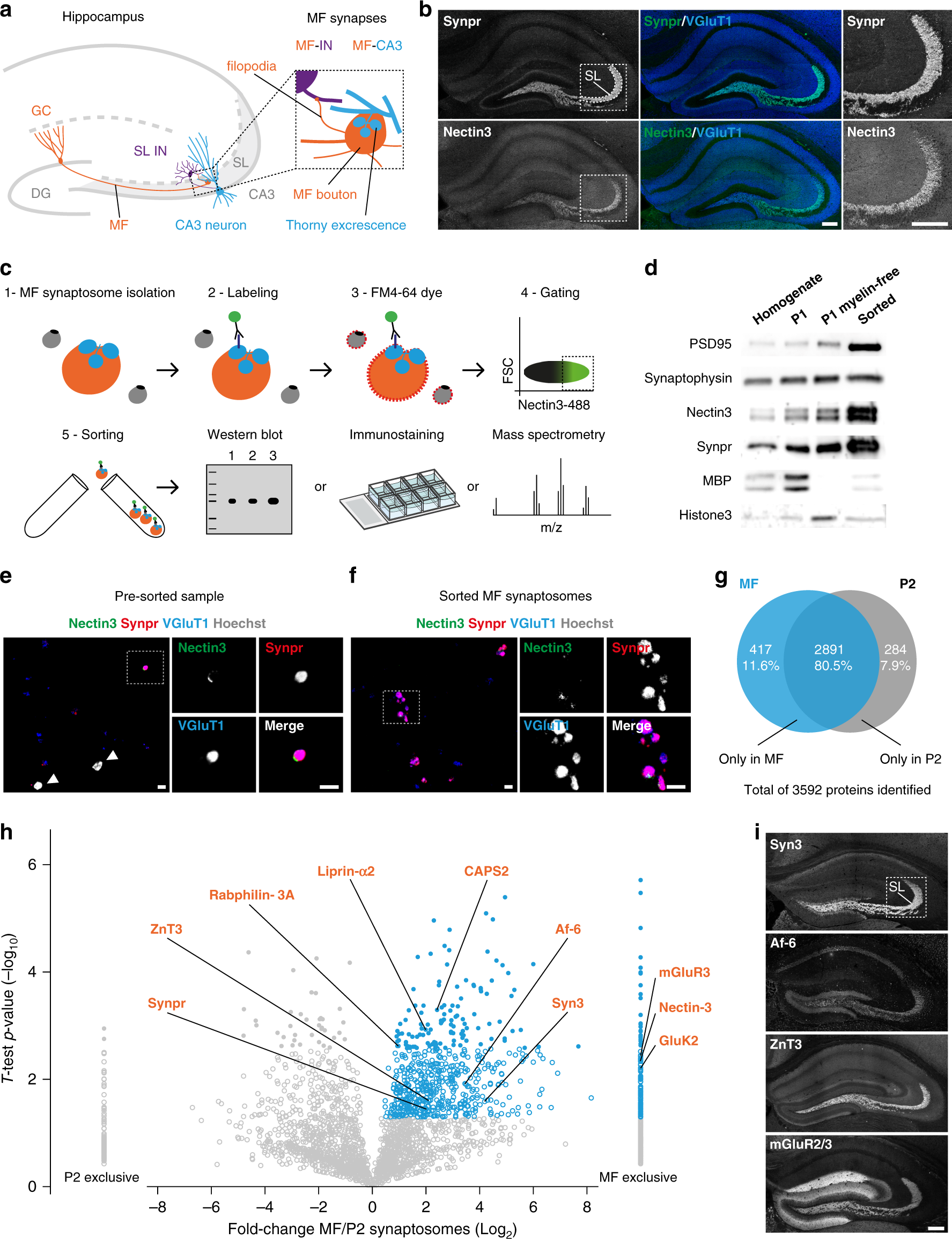 Synapse type-specific proteomic dissection identifies IgSF8 as a25 fevereiro 2025
Synapse type-specific proteomic dissection identifies IgSF8 as a25 fevereiro 2025 -
High throughput stream ingestion to Azure Synapse - Azure25 fevereiro 2025
-
 Scientists discover unique imaging technique to view synapse proteins25 fevereiro 2025
Scientists discover unique imaging technique to view synapse proteins25 fevereiro 2025 -
 ASRock x Razer25 fevereiro 2025
ASRock x Razer25 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 funny yeat profile pics|TikTok Search25 fevereiro 2025
funny yeat profile pics|TikTok Search25 fevereiro 2025 -
faculdadefemaf (@faculdadefemaf1) / X25 fevereiro 2025
-
 littlealchemy2|TikTok Search25 fevereiro 2025
littlealchemy2|TikTok Search25 fevereiro 2025 -
shadow the hedgehog intj|TikTok Search25 fevereiro 2025
-
 Comunidades bizarras do Discord25 fevereiro 2025
Comunidades bizarras do Discord25 fevereiro 2025 -
 30+ Desenhos da Barbie para imprimir e colorir - Como fazer em casa Páginas para colorir de unicórnio, Desenho animado da barbie, Esboços de cartoons25 fevereiro 2025
30+ Desenhos da Barbie para imprimir e colorir - Como fazer em casa Páginas para colorir de unicórnio, Desenho animado da barbie, Esboços de cartoons25 fevereiro 2025 -
 Warner Bros. CEO Hints at Future Video Games for Superman & More - Bell of Lost Souls25 fevereiro 2025
Warner Bros. CEO Hints at Future Video Games for Superman & More - Bell of Lost Souls25 fevereiro 2025 -
Spider Man edição jogo do ano PS4 LACRADO25 fevereiro 2025
-
 CyberpowerPC Gamer Supreme Liquid Cool Gaming PC, AMD Ryzen 9 7900X 4.7GHz 3.8GHz, GeForce RTX 4070 12GB, 16GB DDR5, 2TB NVMe SSD, Wi-Fi Ready25 fevereiro 2025
CyberpowerPC Gamer Supreme Liquid Cool Gaming PC, AMD Ryzen 9 7900X 4.7GHz 3.8GHz, GeForce RTX 4070 12GB, 16GB DDR5, 2TB NVMe SSD, Wi-Fi Ready25 fevereiro 2025 -
 extends (for Explores), Looker25 fevereiro 2025
extends (for Explores), Looker25 fevereiro 2025




