Pathogens, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 janeiro 2025
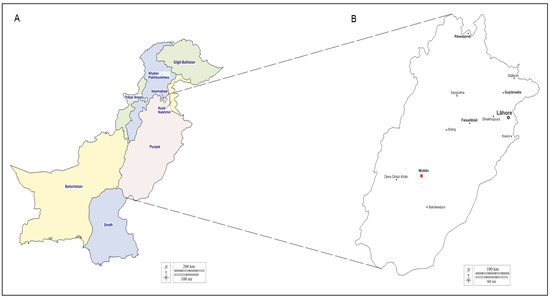
Bovine anaplasmosis is a tick-borne disease caused by an obligate intercellular Gram-negative bacterium named Anaplasma (A.) marginale. In this study, we report the seasonal prevalence, potentially associated risk factors and phylogeny of A. marginale in cattle of three different breeds from Multan District, Southern Punjab, Pakistan. A total of 1020 blood samples (crossbred, n = 340; Holstein Friesian, n = 340; and Sahiwal breed, n = 340) from apparently healthy cattle were collected on a seasonal basis from March 2020 to April 2021. Based on PCR amplification of the msp5 partial sequence, overall, the A. marginale prevalence rate was estimated at 11.1% (113/1020) of the analyzed cattle samples. According to seasons, the highest prevalence rate was observed in autumn (16.5%), followed by winter (10.6%) and summer (9.8%), and the lowest was recorded in the spring (7.5%). The crossbred and Sahiwal cattle were the most susceptible to A. marginale infection, followed by Holstein Friesian cattle (7.9%). Analysis of epidemiological factors revealed that cattle reared on farms where dairy animals have tick loads, dogs coinhabit with cattle and dogs have tick loads have a higher risk of being infected with A. marginale. In addition, it was observed that white blood cell, lymphocyte (%), monocyte (%), hematocrit, mean corpuscular hemoglobin and mean corpuscular hemoglobin concentrations were significantly disturbed in A. marginale-positive cattle compared with non-infested cattle. Genetic analysis of nucleotide sequences and a phylogenetic study based on msp5 partial sequencing demonstrated that this gene appears to be highly conserved among our isolates and those infecting apparently healthy cattle from geographically diverse worldwide regions. The presented data are crucial for estimating the risk of bovine anaplasmosis in order to develop integrated control policies against bovine anaplasmosis and other tick-borne diseases infecting cattle in the country.
Bacteria - Definition and Examples - Biology Online Dictionary
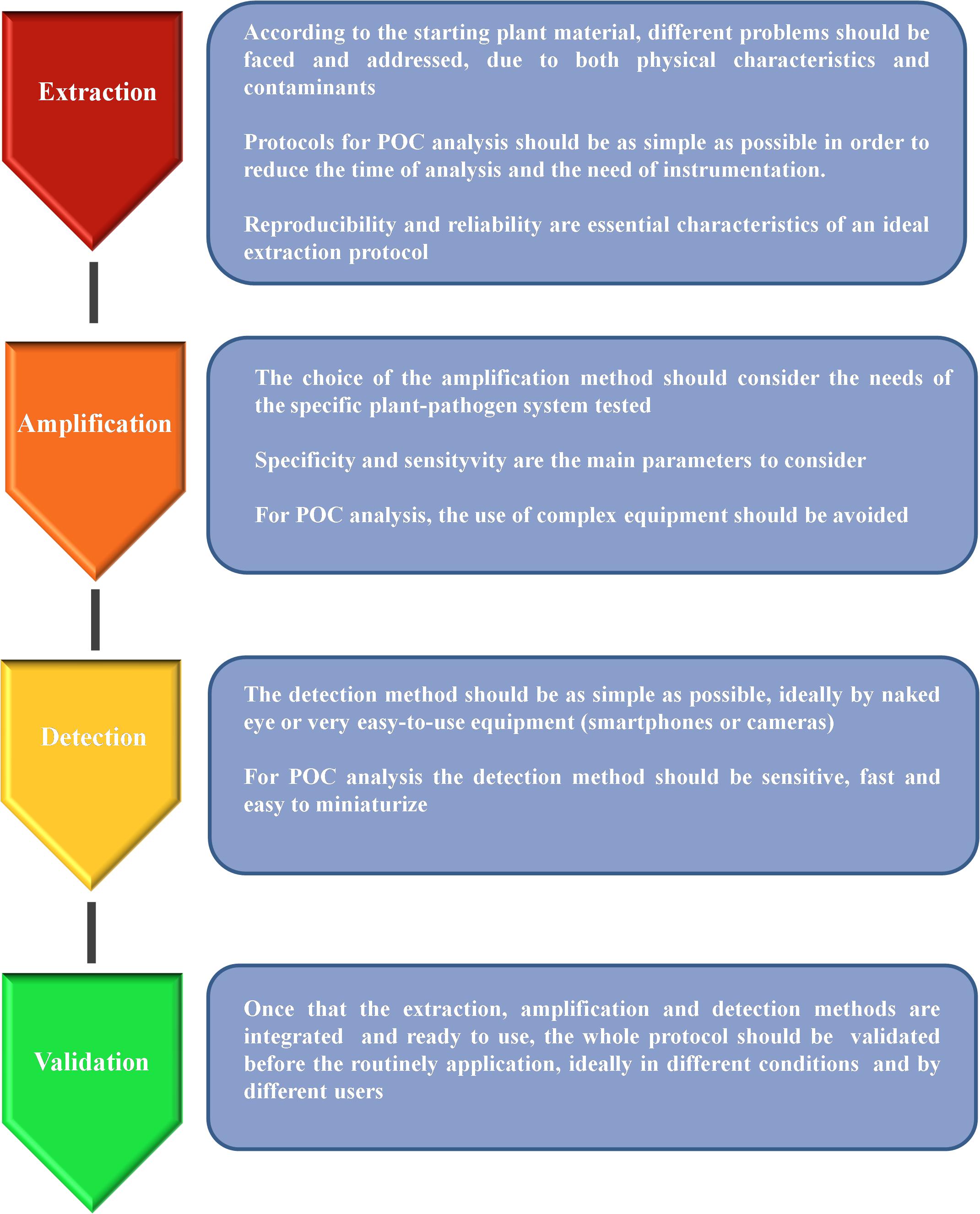
Frontiers Molecular Approaches for Low-Cost Point-of-Care

Solved 1. What is epithelia, what is an example of

Pathogens Vectors & Illustrations for Free Download
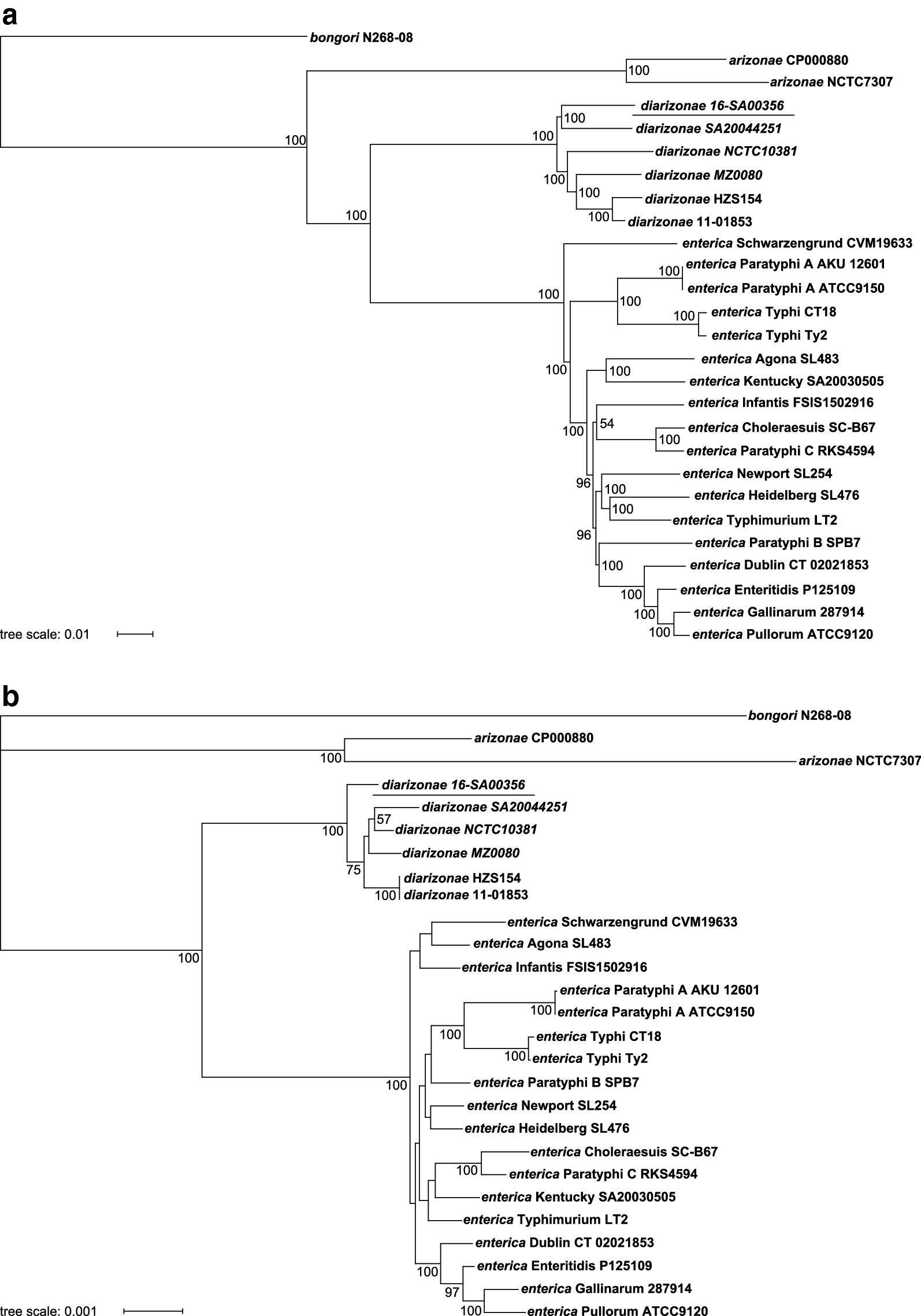
First complete genome sequence and comparative analysis of

Features of pathogens. There are various types of pathogens
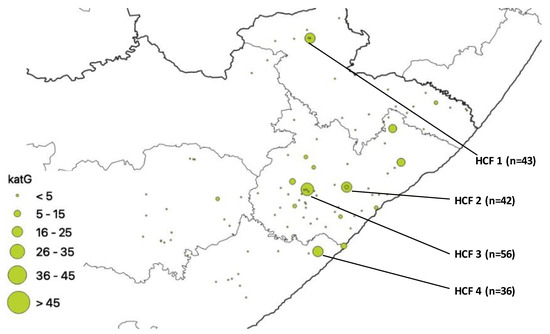
Hcf Practice Maps - Colaboratory

Bloodborne Pathogens Certificate Templates 6 FREE Designs

Global mortality associated with 33 bacterial pathogens in 2019: a
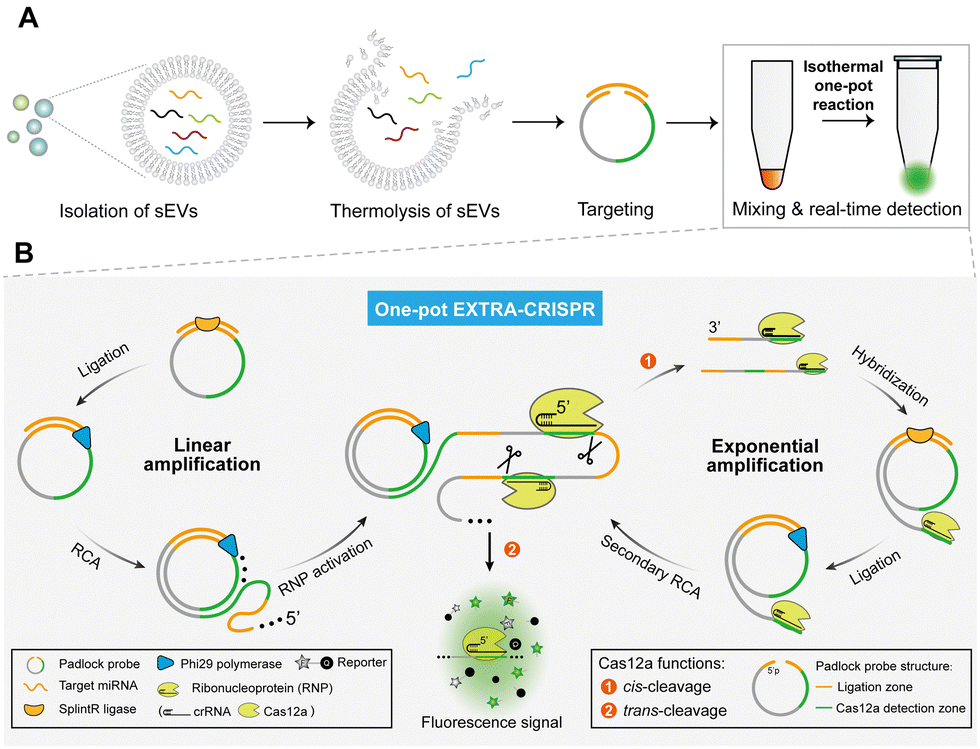
Publications – Zeng Lab

Read et al. warned us 2015 using chickens (Marek's disease) that

Microbial Minimalism: Genome Reduction in Bacterial Pathogens

Pathogen Genomics in Public Health

A culture-free biphasic approach for sensitive and rapid detection
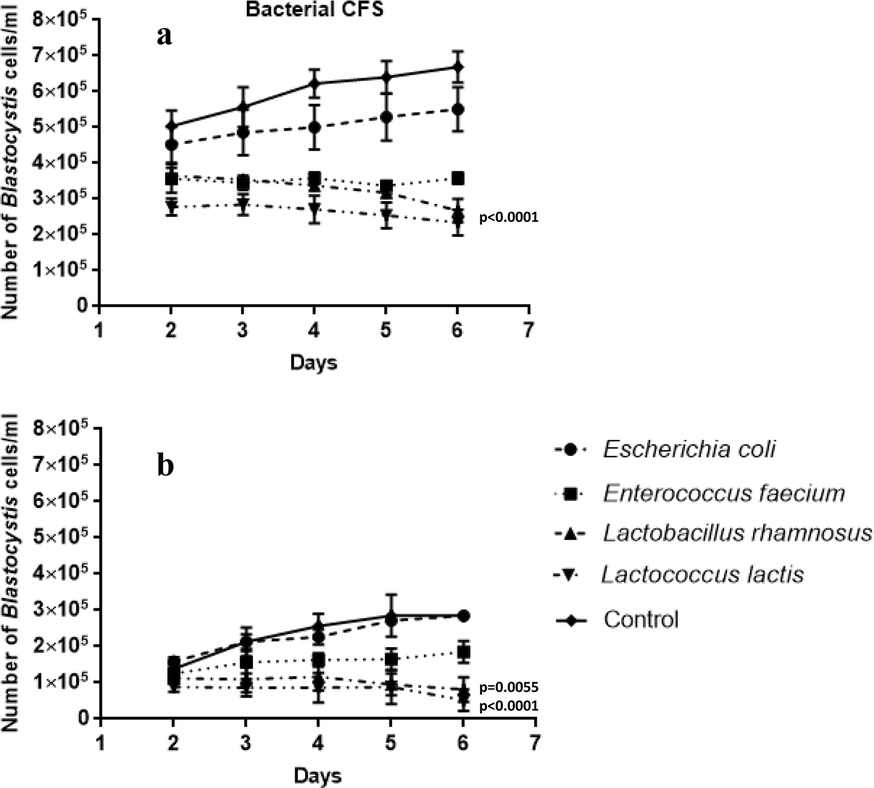
The influence of probiotic bacteria and human gut microorganisms
Recomendado para você
-
 Lavoisier: Agendamento de exames e vacinas pelo Nav22 janeiro 2025
Lavoisier: Agendamento de exames e vacinas pelo Nav22 janeiro 2025 -
Agendamento online de exames e vacinas22 janeiro 2025
-
 Coronavirus (COVID-19) Testing22 janeiro 2025
Coronavirus (COVID-19) Testing22 janeiro 2025 -
 64° Congresso Brasileiro de Oftalmologia22 janeiro 2025
64° Congresso Brasileiro de Oftalmologia22 janeiro 2025 -
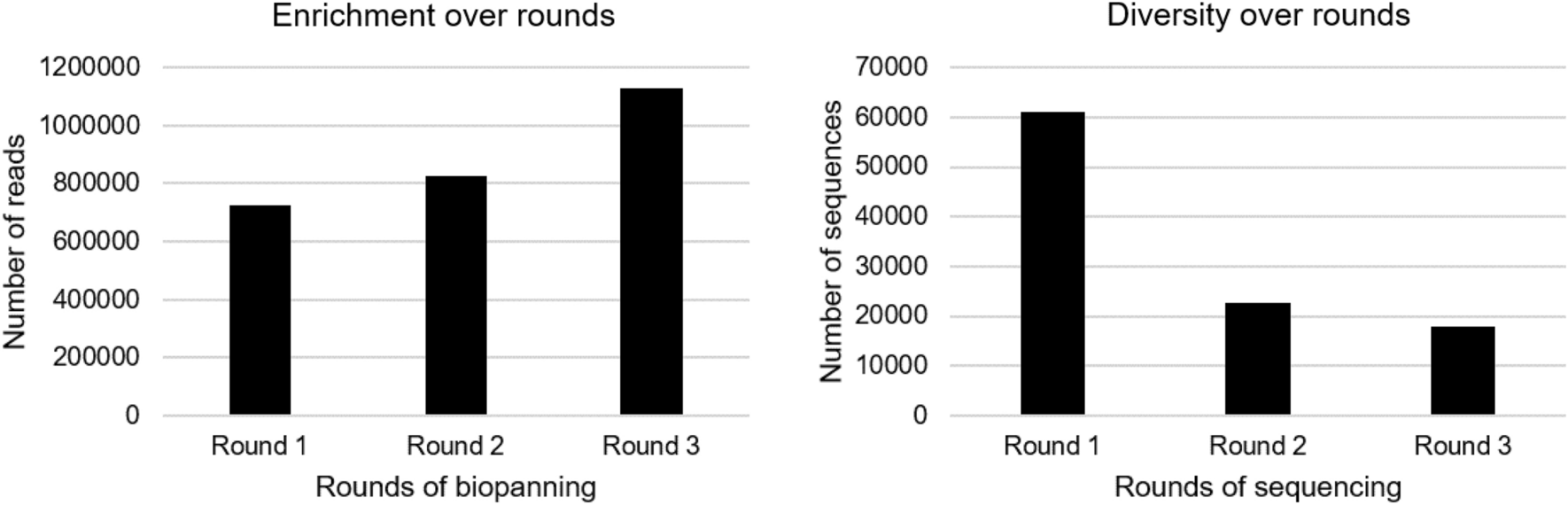 Identification of a novel peptide ligand for the cancer-specific receptor mutation EGFRvIII using high-throughput sequencing of phage-selected peptides22 janeiro 2025
Identification of a novel peptide ligand for the cancer-specific receptor mutation EGFRvIII using high-throughput sequencing of phage-selected peptides22 janeiro 2025 -
 Tem novidade na área! Ampliamos a rede de laboratórios credenciados - Notícias22 janeiro 2025
Tem novidade na área! Ampliamos a rede de laboratórios credenciados - Notícias22 janeiro 2025 -
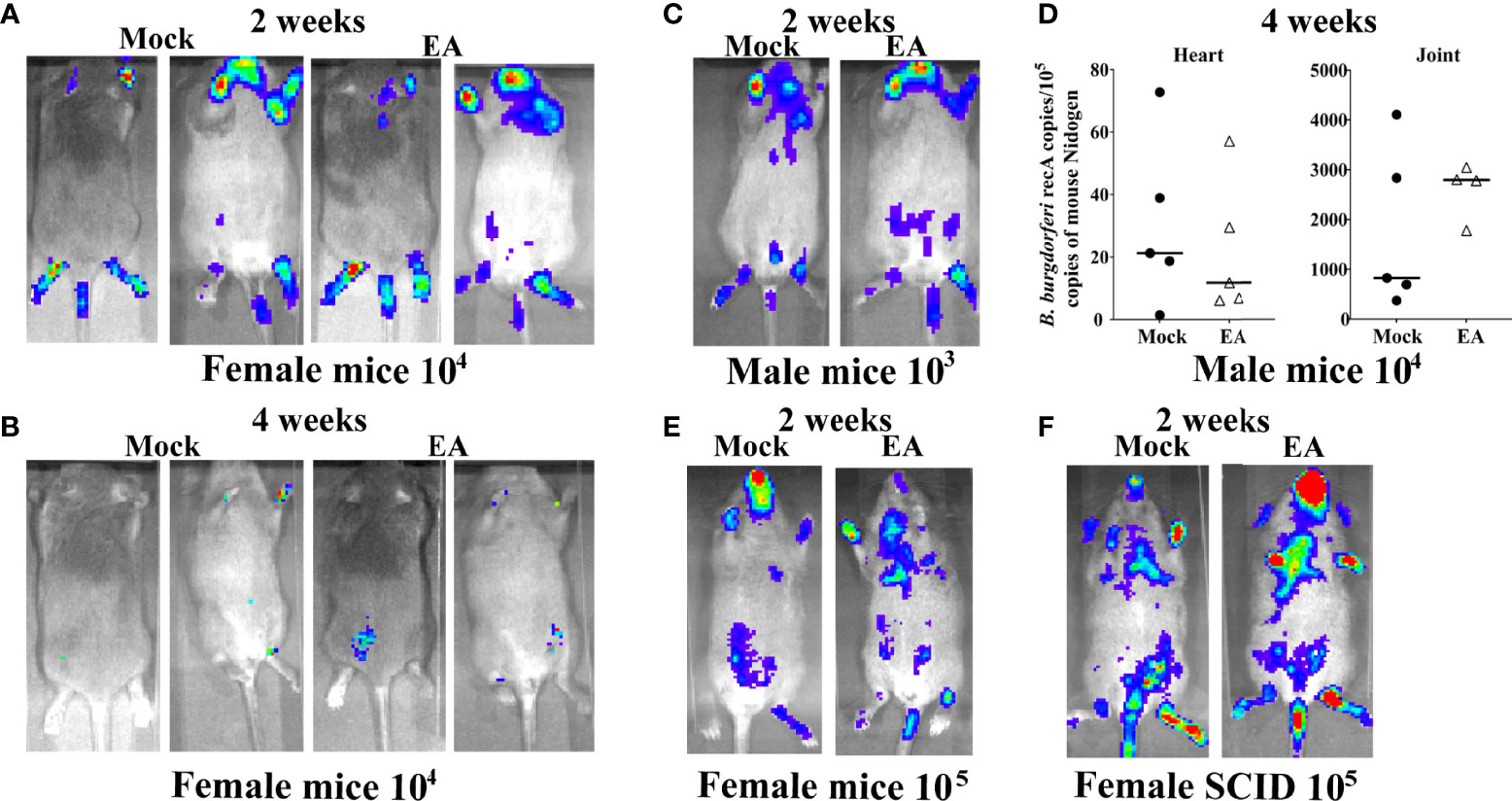 Frontiers Sciatic–Vagal Nerve Stimulation by Electroacupuncture Alleviates Inflammatory Arthritis in Lyme Disease-Susceptible C3H Mice22 janeiro 2025
Frontiers Sciatic–Vagal Nerve Stimulation by Electroacupuncture Alleviates Inflammatory Arthritis in Lyme Disease-Susceptible C3H Mice22 janeiro 2025 -
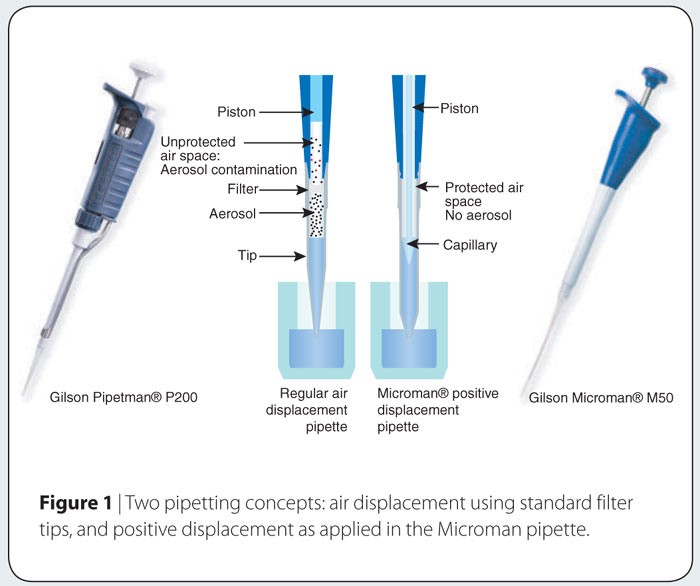 Contamination-pipetting: relative efficiency of filter tips compared to Microman® positive displacement pipette22 janeiro 2025
Contamination-pipetting: relative efficiency of filter tips compared to Microman® positive displacement pipette22 janeiro 2025 -
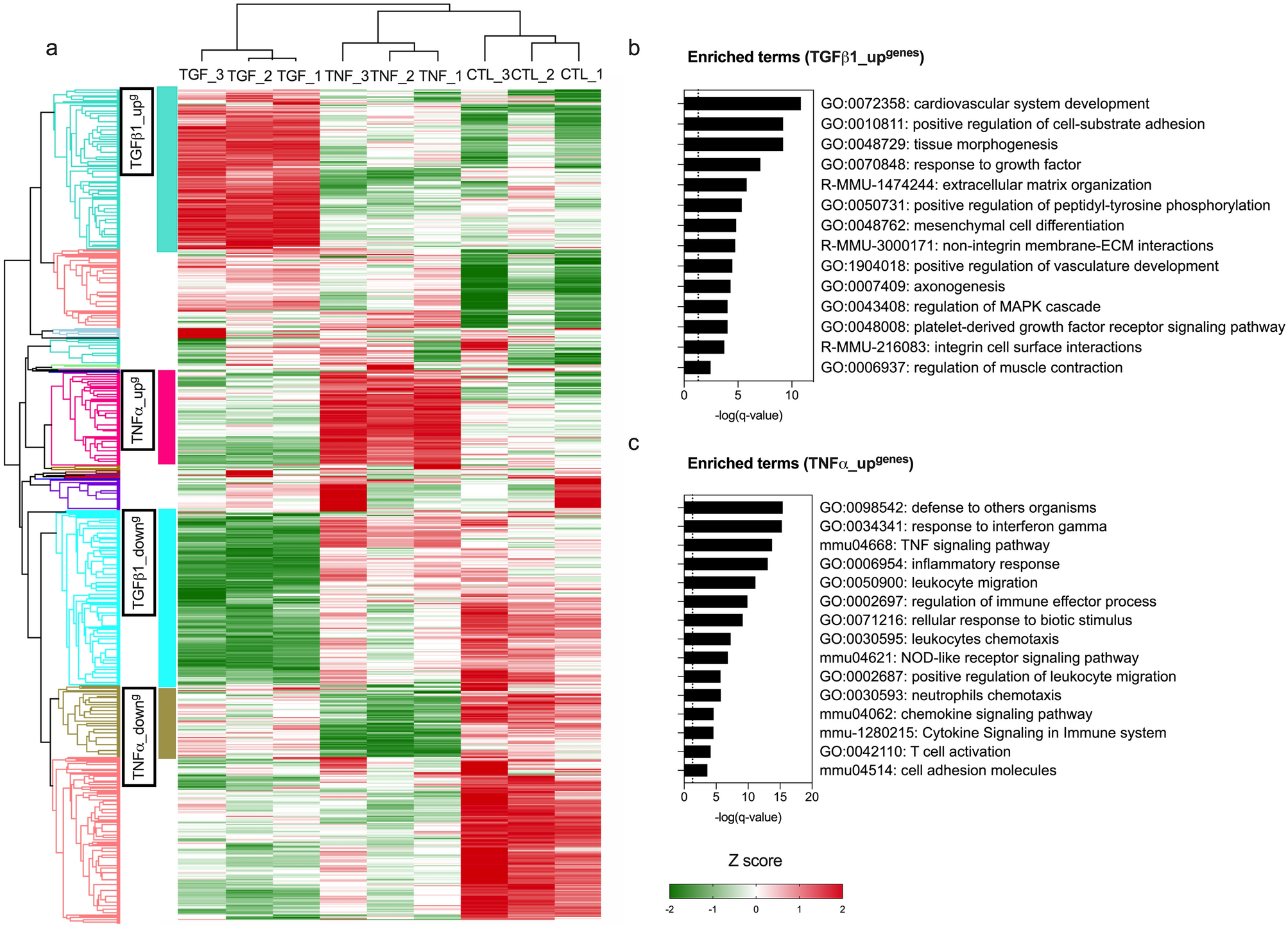 Simple gene signature to assess murine fibroblast polarization22 janeiro 2025
Simple gene signature to assess murine fibroblast polarization22 janeiro 2025 -
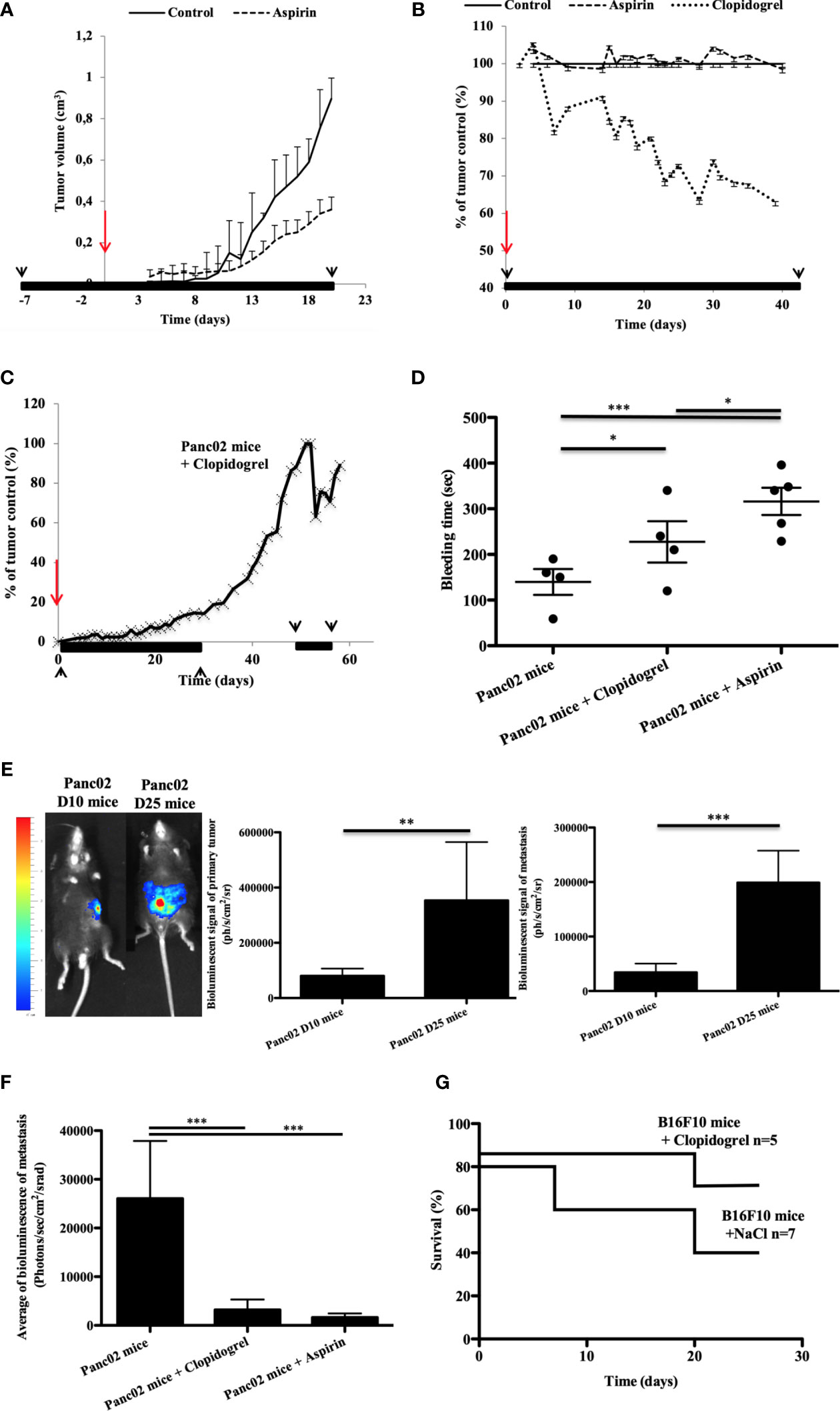 Frontiers P2RY12-Inhibitors Reduce Cancer-Associated Thrombosis and Tumor Growth in Pancreatic Cancers22 janeiro 2025
Frontiers P2RY12-Inhibitors Reduce Cancer-Associated Thrombosis and Tumor Growth in Pancreatic Cancers22 janeiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2021/D/D/FCF7YpSselSC124bnXQw/1.-obs-studio.jpg) Como fazer live pelo PC? Veja lista com sete opções de programas22 janeiro 2025
Como fazer live pelo PC? Veja lista com sete opções de programas22 janeiro 2025 -
Family Practice Physician «Dr. Neri F. Franzon, MD», reviews and photos22 janeiro 2025
-
 Eyes - The Horror Game APK v6.0.8 Free Download - APK4Fun22 janeiro 2025
Eyes - The Horror Game APK v6.0.8 Free Download - APK4Fun22 janeiro 2025 -
 Jogo de Cozinha Ponto Cruz - Patinho em Tecido Xadrez Marrom em Promoção na Americanas22 janeiro 2025
Jogo de Cozinha Ponto Cruz - Patinho em Tecido Xadrez Marrom em Promoção na Americanas22 janeiro 2025 -
![Marvel's The New Mutants UHD [Blu-ray] [2020] [Region Free] [4K UHD] : Movies & TV](https://m.media-amazon.com/images/W/MEDIAX_792452-T2/images/I/81qBK11FDTL._AC_UF350,350_QL80_.jpg) Marvel's The New Mutants UHD [Blu-ray] [2020] [Region Free] [4K UHD] : Movies & TV22 janeiro 2025
Marvel's The New Mutants UHD [Blu-ray] [2020] [Region Free] [4K UHD] : Movies & TV22 janeiro 2025 -
 Ice Nine Kills – The Silver Scream (2021, Silver, Vinyl) - Discogs22 janeiro 2025
Ice Nine Kills – The Silver Scream (2021, Silver, Vinyl) - Discogs22 janeiro 2025 -
 The Battle of Baltimore22 janeiro 2025
The Battle of Baltimore22 janeiro 2025 -
:no_upscale()/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_asset/file/22536576/E17thxTWEAceD6F.jpg) Victoria 3 confirmed with PDXCon 2021 announcement - Polygon22 janeiro 2025
Victoria 3 confirmed with PDXCon 2021 announcement - Polygon22 janeiro 2025 -
 Novo jogo de Prince of Persia anunciado, chegando 18 de Janeiro de 2024. : r/gamesEcultura22 janeiro 2025
Novo jogo de Prince of Persia anunciado, chegando 18 de Janeiro de 2024. : r/gamesEcultura22 janeiro 2025 -
 Grupo Lpoint® - Converse Chuck Taylor All Star White M7652c22 janeiro 2025
Grupo Lpoint® - Converse Chuck Taylor All Star White M7652c22 janeiro 2025