Sustainability, Free Full-Text
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 20 fevereiro 2025
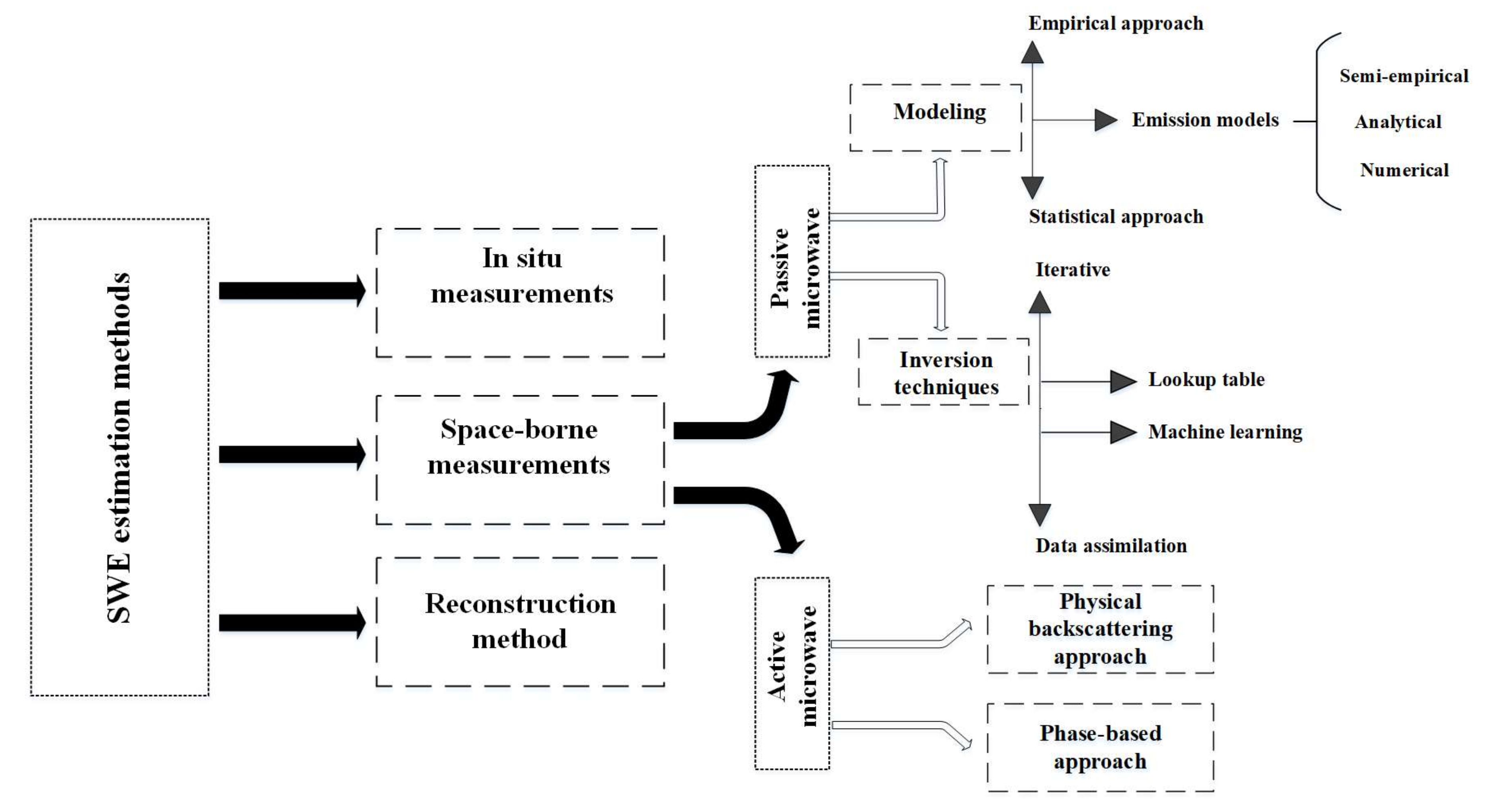
The snow depth or snow water equivalent affects water, carbon, and energy cycles as well as surface–atmosphere interactions. Therefore, the global monitoring of spatiotemporal changes in snow water equivalent is a crucial issue, which is performed by characterizing the macrophysical, microstructural, optical, and thermal characteristics of the snowpack. This paper is a review of the retrieval methods of snow water equivalent in three main categories, including in situ measurements, reconstruction approaches, and space-borne measurements, along with their basic concepts, advantages, and uncertainties. Since satellite observations are the most important tool used to detect snow properties, the paper focuses on inversion models and techniques using microwave remote sensing. The inversion models, based on various theoretical foundations, are classified into empirical, statistical, and physical (emission) models, and the techniques are described in four groups: iterative methods, lookup table, machine learning, and data assimilation approaches. At the end, the available global and regional gridded products providing the spatiotemporal maps of snow water equivalent with different resolutions are presented, as well as approaches for improving the snow data.

Energy Efficiency & Sustainability Experts

Sustainability Saint Francis University

Sustainability, Full Stop

Sustainability Strategic Plan
Sustainability, Free Full-Text
IFRS - FSA Credential
Home - Global Footprint Network

Environmental, Sustainable Papers LLC

MIT Sloan Management Review
Recomendado para você
-
Wcom Informática20 fevereiro 2025
-
 Casa de Condomínio 28 m² em Vila Franca em São Paulo, por R$ 80020 fevereiro 2025
Casa de Condomínio 28 m² em Vila Franca em São Paulo, por R$ 80020 fevereiro 2025 -
🏡Casa em Condomínio Araçoiaba da Serra-SP 📐800 m² Terreno 📐33220 fevereiro 2025
-
 Casas em leilão em Sorocaba - SP - Imovelweb20 fevereiro 2025
Casas em leilão em Sorocaba - SP - Imovelweb20 fevereiro 2025 -
/media/movies/covers/2016/07/purple-rain_t6061_a1WCom0.jpg) Purple Rain - 27 de Julho de 198420 fevereiro 2025
Purple Rain - 27 de Julho de 198420 fevereiro 2025 -
 Remote Sensing January 2017 - Browse Articles20 fevereiro 2025
Remote Sensing January 2017 - Browse Articles20 fevereiro 2025 -
 Casas com cozinha à venda em Jardim Residencial Mont Blanc20 fevereiro 2025
Casas com cozinha à venda em Jardim Residencial Mont Blanc20 fevereiro 2025 -
 Coming Soon - Cartel extra grande de 13 onzas de vinilo resistente de una cara con ojales de metal : Productos de Oficina20 fevereiro 2025
Coming Soon - Cartel extra grande de 13 onzas de vinilo resistente de una cara con ojales de metal : Productos de Oficina20 fevereiro 2025 -
André Silva - Gerente de produtos - BdV Behrens GmbH20 fevereiro 2025
-
Douglas Reis Martins - Gerente de manutenção - Ajinomoto do Brasil Industria e Comércio de Alimentos Ltda.20 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Regras que as damas de companhia da Realeza Britânica devem seguir20 fevereiro 2025
Regras que as damas de companhia da Realeza Britânica devem seguir20 fevereiro 2025 -
 Sonic the Hedgehog - Sonic 1 - Japan Comic Cover by PaperBandicoot on DeviantArt20 fevereiro 2025
Sonic the Hedgehog - Sonic 1 - Japan Comic Cover by PaperBandicoot on DeviantArt20 fevereiro 2025 -
 DANMACHI 4 TEMPORADA EP 4 LEGENDADO PT-BR! DATA DE LANÇAMENTO20 fevereiro 2025
DANMACHI 4 TEMPORADA EP 4 LEGENDADO PT-BR! DATA DE LANÇAMENTO20 fevereiro 2025 -
 A Noiva do Mago Ancião (Mahoutsukai no Yome) - Cinem(ação): filmes, podcasts, críticas e tudo sobre cinema20 fevereiro 2025
A Noiva do Mago Ancião (Mahoutsukai no Yome) - Cinem(ação): filmes, podcasts, críticas e tudo sobre cinema20 fevereiro 2025 -
 Alakazam (Pokémon) - Bulbapedia, the community-driven Pokémon20 fevereiro 2025
Alakazam (Pokémon) - Bulbapedia, the community-driven Pokémon20 fevereiro 2025 -
 Dia de craque jogadores mirins de Dourados e região terão a20 fevereiro 2025
Dia de craque jogadores mirins de Dourados e região terão a20 fevereiro 2025 -
 A MENINA COM VERGONHA DA MÃE MANDRAKE20 fevereiro 2025
A MENINA COM VERGONHA DA MÃE MANDRAKE20 fevereiro 2025 -
 gradle - Right click and create JUnit tests in Android Studio20 fevereiro 2025
gradle - Right click and create JUnit tests in Android Studio20 fevereiro 2025 -
Trends International Call Of Duty: Modern Warfare 2 - Ghost Emblem Framed Wall Poster Prints White Framed Version 14.725 X 22.375 : Target20 fevereiro 2025
-
 QUIZ - Conhecimentos Gerais - APRENDA na real20 fevereiro 2025
QUIZ - Conhecimentos Gerais - APRENDA na real20 fevereiro 2025




