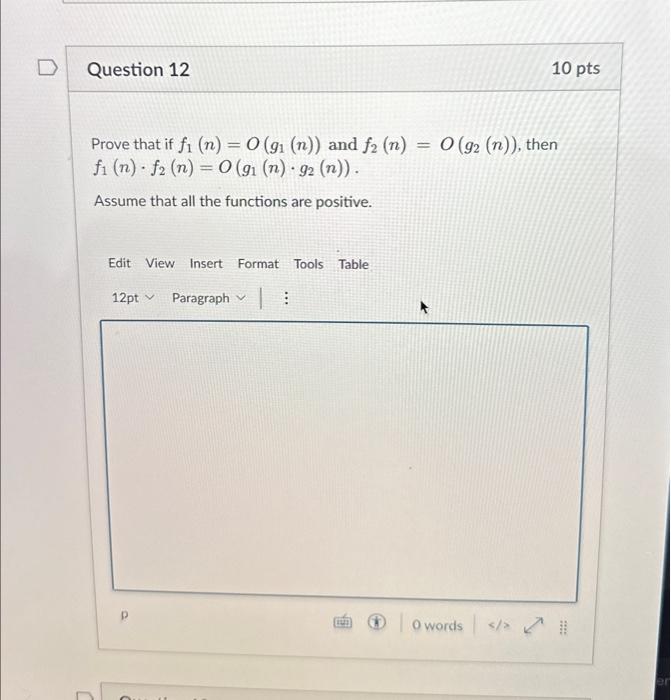
Replicatively senescent cells are arrested in G1 and G2 phases - Figure F1
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 19 dezembro 2024
Senescent human fibroblast cultures contain a large fraction of putative G2-arrested cells with 4N DNA content. (A) Propidium iodide (PI) staining and flow cyctometric analysis of HCA2 normal human foreskin fibroblasts. Cells entered senescence at PD73. (B) PI staining of replicatively senescent human lung fibroblasts WI-38, and IMR-90 at PDs 73 and 68 respectively. (C) The fraction of 4N cells in senescent cell population does not diminish with time. Replicatively senescent HCA2 cells were analyzed by PI staining at weekly intervals for 10 weeks stating from the onset of senescence.
Key elements of cellular senescence involve transcriptional
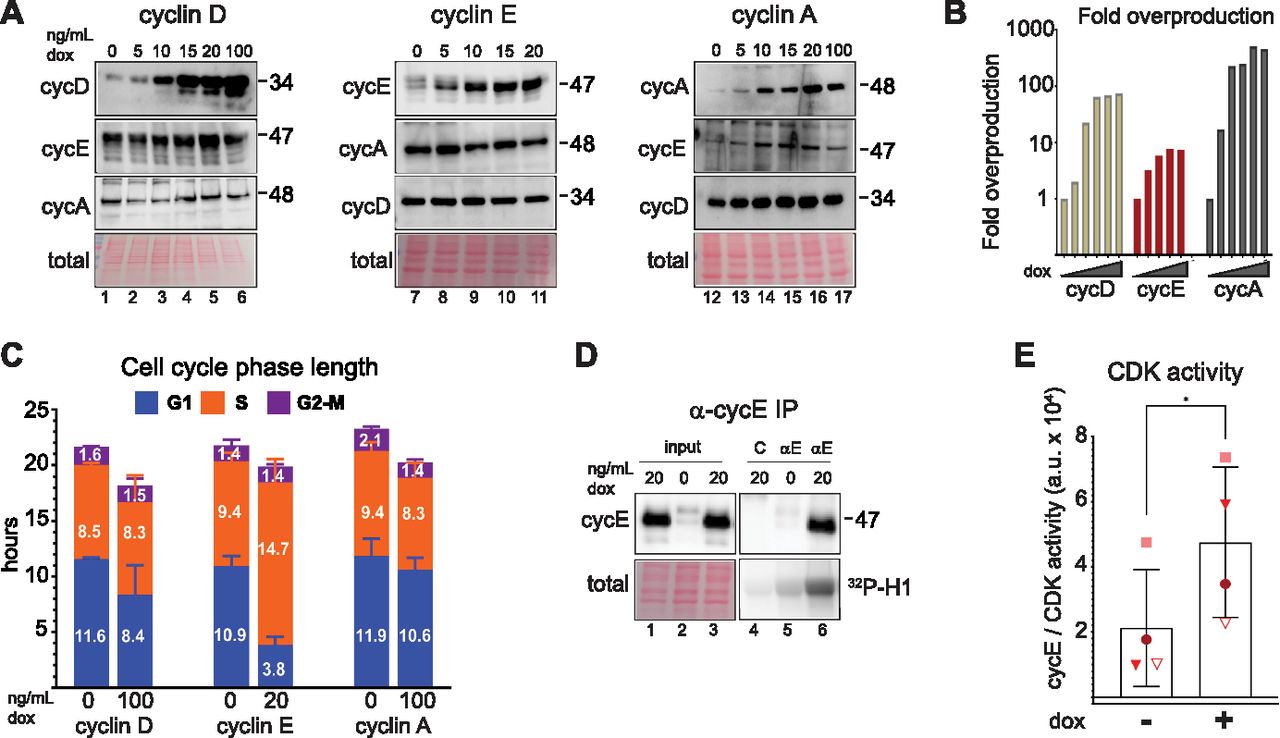
Quantitative profiling of adaptation to cyclin E overproduction

Full article: Dysregulated endolysosomal trafficking in cells

Figure 3 from SUN1 silencing inhibits cell growth through G0/G1

Cells were arrested in G0/G1 phase under hypoxia. a–d Cell-cycle

G1/S Transition - an overview

Telomeric dysfunction triggers an unstable growth arrest leading
Single-cell transcriptomic analysis uncovers diverse and dynamic

Exploiting replicative stress in gynecological cancers as a

Necessary and Sufficient Role for a Mitosis Skip in Senescence

G1 and G2: What Happens in the Growth Phases of The Cell Cycle?
Recomendado para você
-
 F1 Car Simplify Transform】Transformers G1 Series Third party custom Mirage DX9 D03 Car Robot Toys19 dezembro 2024
F1 Car Simplify Transform】Transformers G1 Series Third party custom Mirage DX9 D03 Car Robot Toys19 dezembro 2024 -
 Power HD Aluminum G1 High Stability Gyro Red For RC Car Drift F1 Touring On Road19 dezembro 2024
Power HD Aluminum G1 High Stability Gyro Red For RC Car Drift F1 Touring On Road19 dezembro 2024 -
 BenQ G1 digital camera boasts F1.8 lens, swivel-screen and modest price tag19 dezembro 2024
BenQ G1 digital camera boasts F1.8 lens, swivel-screen and modest price tag19 dezembro 2024 -
 SKF LAPF F1/4 Tube Connection Female G1/419 dezembro 2024
SKF LAPF F1/4 Tube Connection Female G1/419 dezembro 2024 -
 X20T8373 Vizio Stand Legs, X20T8373, X20T837301200000LX, E75-F1, V705-G1, V705-J01, V705X-J0119 dezembro 2024
X20T8373 Vizio Stand Legs, X20T8373, X20T837301200000LX, E75-F1, V705-G1, V705-J01, V705X-J0119 dezembro 2024 -
Solved Prove that if f1(n)=O(g1(n)) and f2(n)=O(g2(n)), then19 dezembro 2024
-
 F1: Lewis Hamilton Wins United States Grand Prix (PHOTOS) - Racing News19 dezembro 2024
F1: Lewis Hamilton Wins United States Grand Prix (PHOTOS) - Racing News19 dezembro 2024 -
Solved 9. Given functions f1,f2,g1,g2 such that19 dezembro 2024
-
 Wide Magazine19 dezembro 2024
Wide Magazine19 dezembro 2024 -
 G1 - G1 jogou: 'F1 2014' traz direção mais precisa, mas freia evolução do game - notícias em Games19 dezembro 2024
G1 - G1 jogou: 'F1 2014' traz direção mais precisa, mas freia evolução do game - notícias em Games19 dezembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
Can I play God of War (any part) on PC? - Quora19 dezembro 2024
-
 Praggnanandhaa loses to Ding Liren in tie-break at Chessable Masters final19 dezembro 2024
Praggnanandhaa loses to Ding Liren in tie-break at Chessable Masters final19 dezembro 2024 -
 Super Action Statue Joseph Joestar - Astro Toy - Anime News Network19 dezembro 2024
Super Action Statue Joseph Joestar - Astro Toy - Anime News Network19 dezembro 2024 -
![AI Enlarger: for Photo & Anime Mod apk [Unlocked][Pro] download - AI Enlarger: for Photo & Anime MOD apk 3.0.4 free for Android.](https://i.git99.com/upload/android/icon/2023/11/05/07dd2ec1e0255daab4e1d08b8bdbc928.jpg) AI Enlarger: for Photo & Anime Mod apk [Unlocked][Pro] download - AI Enlarger: for Photo & Anime MOD apk 3.0.4 free for Android.19 dezembro 2024
AI Enlarger: for Photo & Anime Mod apk [Unlocked][Pro] download - AI Enlarger: for Photo & Anime MOD apk 3.0.4 free for Android.19 dezembro 2024 -
 Just got Roblox on my PS5! : r/roblox19 dezembro 2024
Just got Roblox on my PS5! : r/roblox19 dezembro 2024 -
 Rockwell RED Monster Jam Truck19 dezembro 2024
Rockwell RED Monster Jam Truck19 dezembro 2024 -
 The Idaho College Murders» estreia no Canal ID19 dezembro 2024
The Idaho College Murders» estreia no Canal ID19 dezembro 2024 -
 Fukigen na mononokean tsuzuki19 dezembro 2024
Fukigen na mononokean tsuzuki19 dezembro 2024 -
 Guess ima commit dead : r/memes19 dezembro 2024
Guess ima commit dead : r/memes19 dezembro 2024 -
 Yami Yami No Mi Gifts & Merchandise for Sale19 dezembro 2024
Yami Yami No Mi Gifts & Merchandise for Sale19 dezembro 2024