Differential cellular stiffness contributes to tissue elongation on an expanding surface
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 01 fevereiro 2025


Effect of matrix stiffness on cell height (A) Cell height was

Buckling of an Epithelium Growing under Spherical Confinement - ScienceDirect

Cell–3D matrix interactions: recent advances and opportunities: Trends in Cell Biology

Dynamic changes in epithelial cell packing during tissue morphogenesis - ScienceDirect
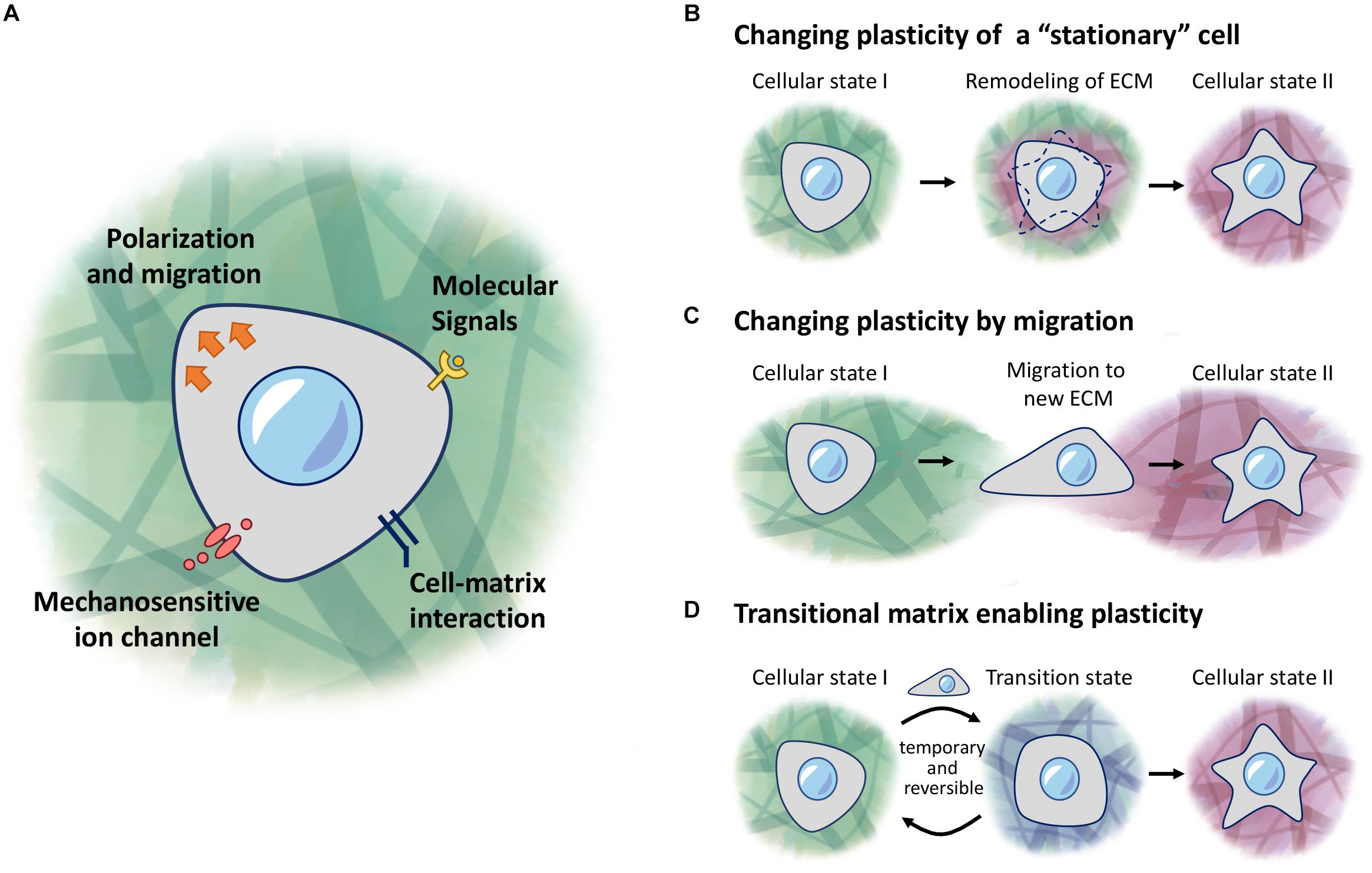
Frontiers Extracellular Matrix and Cellular Plasticity in Musculoskeletal Development
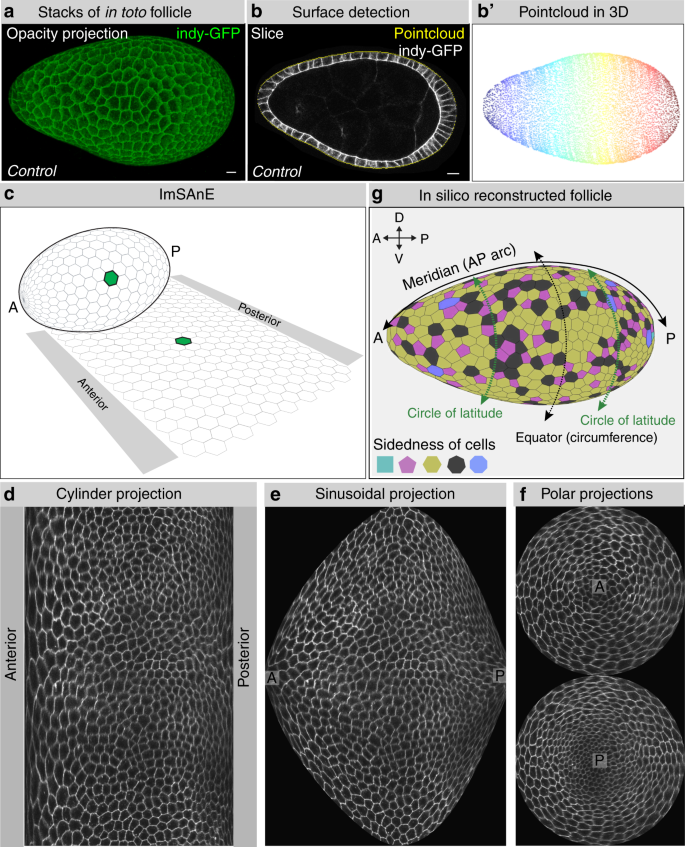
Extracellular matrix stiffness cues junctional remodeling for 3D tissue elongation
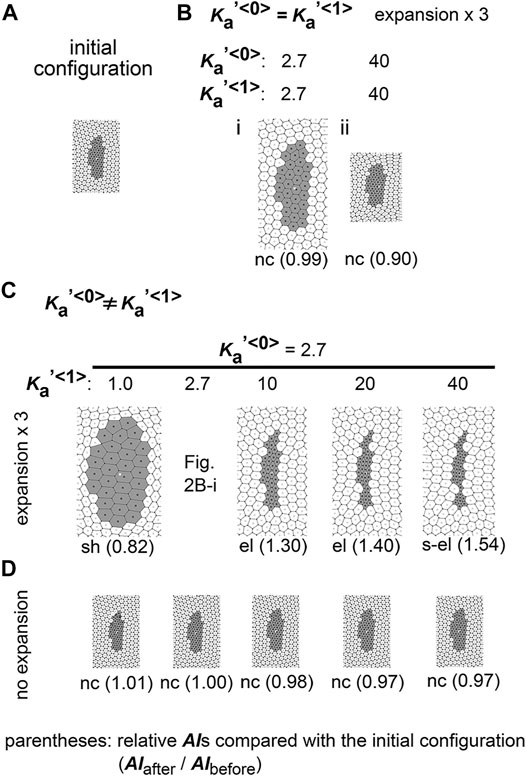
Frontiers Differential Cellular Stiffness Contributes to Tissue Elongation on an Expanding Surface

Stiffness Sensing by Cells
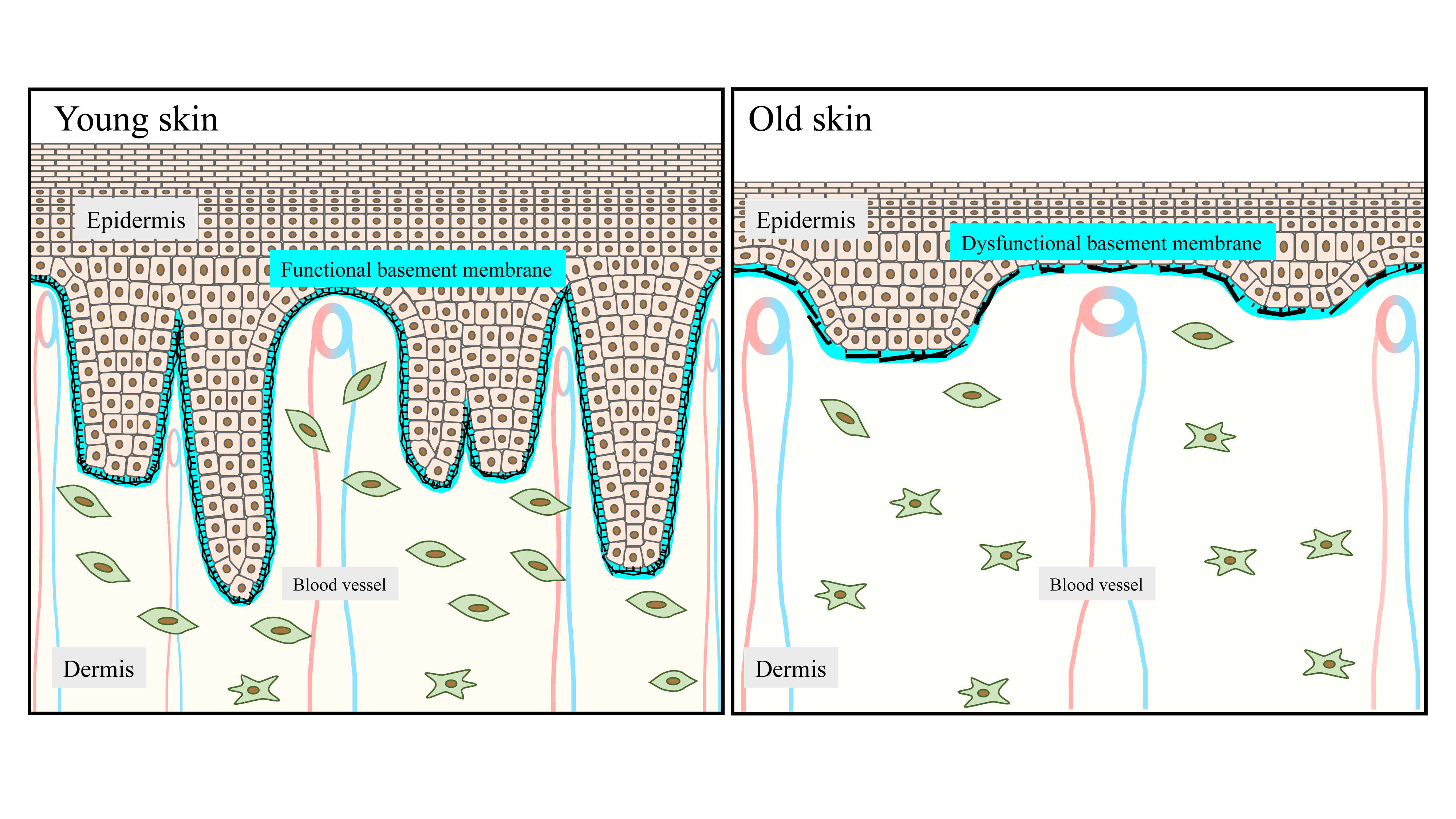
Biomolecules, Free Full-Text
Recomendado para você
-
 Squishy mochi keycaps! : r/keycaps01 fevereiro 2025
Squishy mochi keycaps! : r/keycaps01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Bandai White Squishies01 fevereiro 2025
Bandai White Squishies01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Reese's $25,000 promotion may violate sweepstakes laws01 fevereiro 2025
Reese's $25,000 promotion may violate sweepstakes laws01 fevereiro 2025 -
 JA-RU flarp noise putty scented (1 unit assorted) by ja-ru. squishy sensory toys for easter, autism stress toy, great party favors01 fevereiro 2025
JA-RU flarp noise putty scented (1 unit assorted) by ja-ru. squishy sensory toys for easter, autism stress toy, great party favors01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Making Squishy Circuits From COTS Playdough : 9 Steps (with Pictures) - Instructables01 fevereiro 2025
Making Squishy Circuits From COTS Playdough : 9 Steps (with Pictures) - Instructables01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Blue Cell Phone Squishies for sale01 fevereiro 2025
Blue Cell Phone Squishies for sale01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Mochi Squishy Squishy Toys Decompression Party Favors And Fidget Prizes For Kids Novelty Gift For Adults Drop Delivery Available From Cocofyty, $0.3301 fevereiro 2025
Mochi Squishy Squishy Toys Decompression Party Favors And Fidget Prizes For Kids Novelty Gift For Adults Drop Delivery Available From Cocofyty, $0.3301 fevereiro 2025 -
 Top 10 Greatest RLCS Goals of All Time : r/RocketLeagueEsports01 fevereiro 2025
Top 10 Greatest RLCS Goals of All Time : r/RocketLeagueEsports01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Sold: Mint Nikon F3 - FM Forums01 fevereiro 2025
Sold: Mint Nikon F3 - FM Forums01 fevereiro 2025 -
 squeesh yum® jiggly buddies 3-count, Five Below01 fevereiro 2025
squeesh yum® jiggly buddies 3-count, Five Below01 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 2023 Alpinestars Honda HRC Team MX Gear Set Jersey/Pants Motocross Racing Set01 fevereiro 2025
2023 Alpinestars Honda HRC Team MX Gear Set Jersey/Pants Motocross Racing Set01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Starfield chega com grande nota no Metacritic01 fevereiro 2025
Starfield chega com grande nota no Metacritic01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Marvel Deadpool Chimichangas Rainbow Pint Glass 16 oz01 fevereiro 2025
Marvel Deadpool Chimichangas Rainbow Pint Glass 16 oz01 fevereiro 2025 -
 if a player doesn't have a description, it now reads This user01 fevereiro 2025
if a player doesn't have a description, it now reads This user01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Forever 21 Womens Black Peplum Jacket Size S/P (sku 430)01 fevereiro 2025
Forever 21 Womens Black Peplum Jacket Size S/P (sku 430)01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Right click in Visual Studio 2013 not showing create unit test01 fevereiro 2025
Right click in Visual Studio 2013 not showing create unit test01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Weekend PC Game Deals: Packed with co-op freebies, fresh bundles, and more - Neowin01 fevereiro 2025
Weekend PC Game Deals: Packed with co-op freebies, fresh bundles, and more - Neowin01 fevereiro 2025 -
Anime Trending - Vote for Tomodachi Game here 👉01 fevereiro 2025
-
 𝒔𝒂𝒕𝒐𝒓𝒖 𝒈𝒐𝒋𝒐 𝙞𝙘𝙤𝙣01 fevereiro 2025
𝒔𝒂𝒕𝒐𝒓𝒖 𝒈𝒐𝒋𝒐 𝙞𝙘𝙤𝙣01 fevereiro 2025 -
 Is MultiVersus crossplay?01 fevereiro 2025
Is MultiVersus crossplay?01 fevereiro 2025
