Bayesian modelling for COVID-19 seroprevalence studies
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 22 fevereiro 2025


Age groups that sustain resurging COVID-19 epidemics in the United States
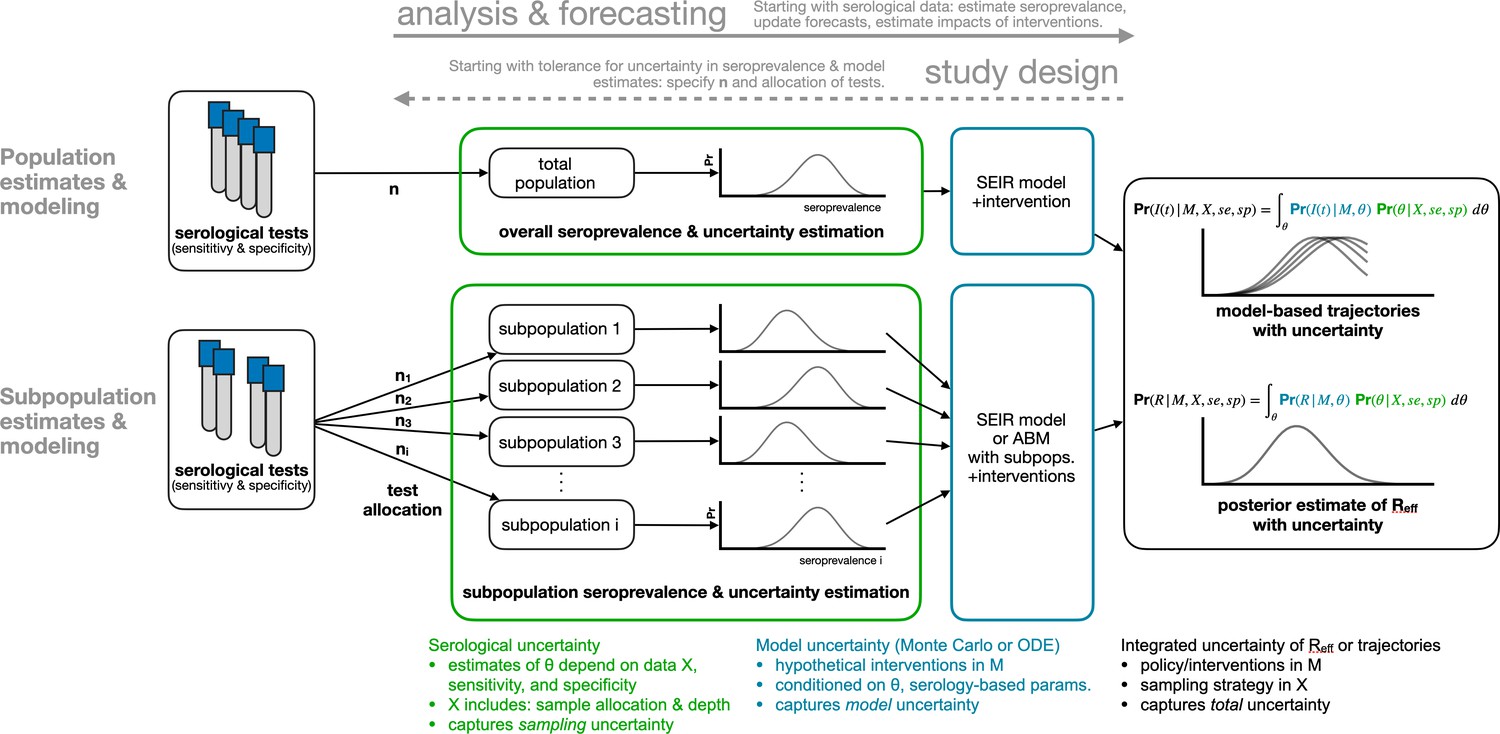
Estimating SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence and epidemiological parameters with uncertainty from serological surveys
Bayesian inference across multiple models suggests a strong increase in lethality of COVID-19 in late 2020 in the UK

Bayesian nonparametric inference for heterogeneously mixing infectious disease models
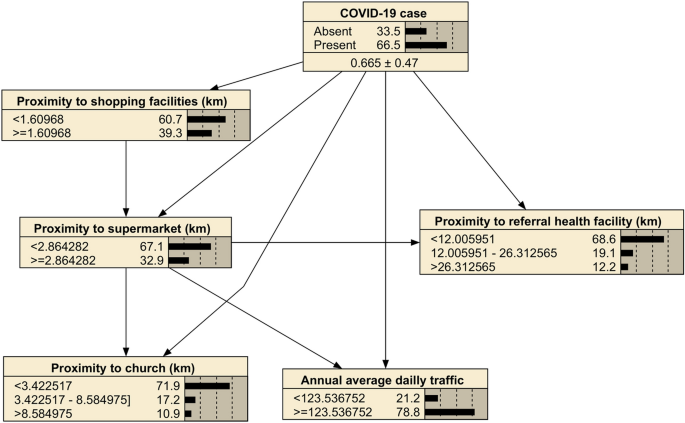
Bayesian network-based spatial predictive modelling reveals COVID-19 transmission dynamics in Eswatini

Update on SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence: regional and worldwide - ScienceDirect

Genomics and epidemiology of the P.1 SARS-CoV-2 lineage in Manaus, Brazil

Seropositivity in blood donors and pregnant women during the first year of SARS‐CoV‐2 transmission in Stockholm, Sweden - Castro Dopico - 2021 - Journal of Internal Medicine - Wiley Online Library
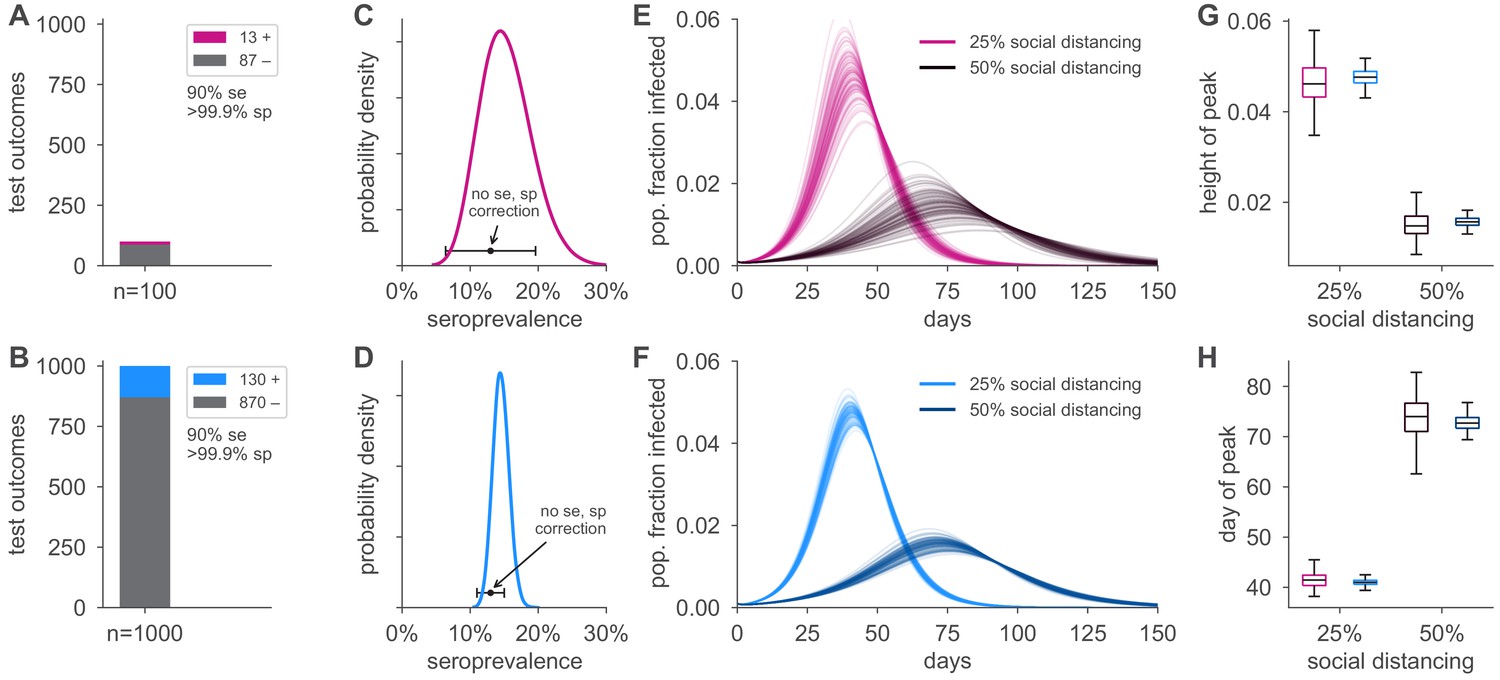
Estimating SARS-CoV-2 seroprevalence and epidemiological parameters with uncertainty from serological surveys
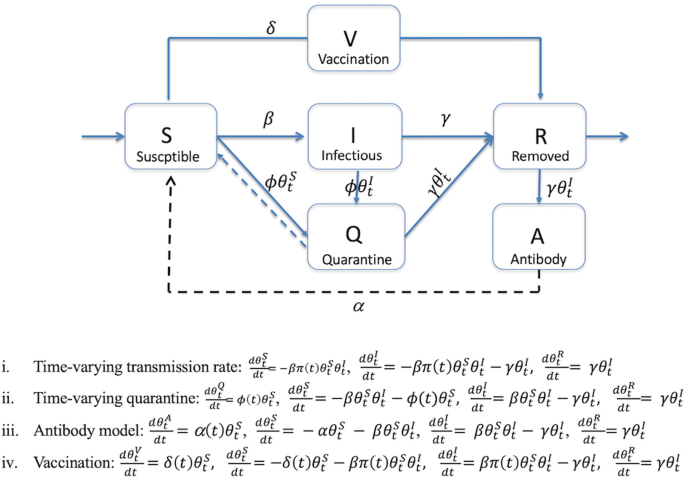
Using outbreak data to estimate the dynamic COVID-19 landscape in Eastern Africa, BMC Infectious Diseases

Seroprevalence of SARS-CoV-2 Antibodies in Children and Adults in St. Louis, Missouri, USA
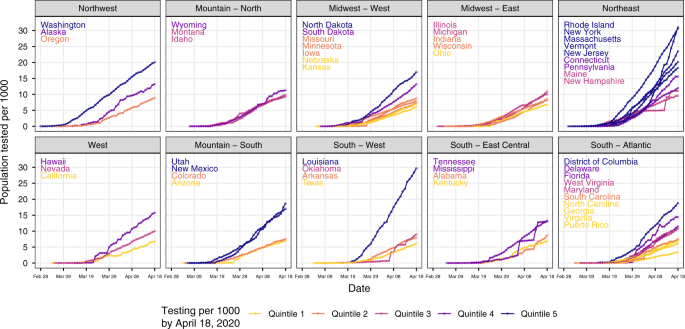
Substantial underestimation of SARS-CoV-2 infection in the United States

Socioeconomic status determines COVID-19 incidence and related mortality in Santiago, Chile

Full article: Bayesian network analysis of Covid-19 data reveals higher infection prevalence rates and lower fatality rates than widely reported

Two Years into the COVID-19 Pandemic: Lessons Learned
Recomendado para você
-
 Doodle check mark e cross mark icon set check list símbolo22 fevereiro 2025
Doodle check mark e cross mark icon set check list símbolo22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Pin de christiane Brant em ITALIA em 202322 fevereiro 2025
Pin de christiane Brant em ITALIA em 202322 fevereiro 2025 -
 PDF) Anxiety and fear related to coronavirus disease 201922 fevereiro 2025
PDF) Anxiety and fear related to coronavirus disease 201922 fevereiro 2025 -
 ThermoTrace Auto-Check Pro Non-Contact Infrared Forehead22 fevereiro 2025
ThermoTrace Auto-Check Pro Non-Contact Infrared Forehead22 fevereiro 2025 -
 PDF Counted Cross Stitch Dogs / Cross Stitch Pattern22 fevereiro 2025
PDF Counted Cross Stitch Dogs / Cross Stitch Pattern22 fevereiro 2025 -
 The Autoimmune Solution: Prevent and Reverse the Full22 fevereiro 2025
The Autoimmune Solution: Prevent and Reverse the Full22 fevereiro 2025 -
 9.900+ ícone De Cancelamento Ilustrações fotos de stock, imagens e22 fevereiro 2025
9.900+ ícone De Cancelamento Ilustrações fotos de stock, imagens e22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Instructions Vetores, Ilustrações e Cliparts para Projetos22 fevereiro 2025
Instructions Vetores, Ilustrações e Cliparts para Projetos22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Check Mark svg , Tick Mark Svg, Check box svg, Cross Mark Svg, Check Mark clipart, cricut & silhouette, vinyl, dxf, ai, pdf, png, eps22 fevereiro 2025
Check Mark svg , Tick Mark Svg, Check box svg, Cross Mark Svg, Check Mark clipart, cricut & silhouette, vinyl, dxf, ai, pdf, png, eps22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Clipart cartoon of a tick check and cross x mark characters - Portugal22 fevereiro 2025
Clipart cartoon of a tick check and cross x mark characters - Portugal22 fevereiro 2025
você pode gostar
-
 Lembrancinha Fortnite22 fevereiro 2025
Lembrancinha Fortnite22 fevereiro 2025 -
 100 Melhores jogadores do mundo, segundo a revista inglesa “Four22 fevereiro 2025
100 Melhores jogadores do mundo, segundo a revista inglesa “Four22 fevereiro 2025 -
 foguinho e água - Desenho de mmcarinhato - Gartic22 fevereiro 2025
foguinho e água - Desenho de mmcarinhato - Gartic22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Rainbow Friends Chapter 2 Kit 10 Pelúcias Brinquedo Roblox em Promoção na Americanas22 fevereiro 2025
Rainbow Friends Chapter 2 Kit 10 Pelúcias Brinquedo Roblox em Promoção na Americanas22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Cyan - Rainbow Friends: Chapter 222 fevereiro 2025
Cyan - Rainbow Friends: Chapter 222 fevereiro 2025 -
melhores lances contra o inter #fy #resenha #gandula #futebol #inter22 fevereiro 2025
-
 Jogos De Tabuleiro 6x1 Ludo Damas Trilha Resta 1 Conecta 4 Cobras22 fevereiro 2025
Jogos De Tabuleiro 6x1 Ludo Damas Trilha Resta 1 Conecta 4 Cobras22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Yuuna and the Haunted Hot Springs The Thrilling Steamy Maze Kiwami22 fevereiro 2025
Yuuna and the Haunted Hot Springs The Thrilling Steamy Maze Kiwami22 fevereiro 2025 -
 Teste os reflexos nas acrobacias incríveis de Moto X3M para smartphones - Android - SAPO Tek22 fevereiro 2025
Teste os reflexos nas acrobacias incríveis de Moto X3M para smartphones - Android - SAPO Tek22 fevereiro 2025 -
 How chess champion Magnus Carlsen broke free to win22 fevereiro 2025
How chess champion Magnus Carlsen broke free to win22 fevereiro 2025
