Performance of Brain-Injured versus Non-Brain-Injured Individuals on Three Versions of the Category Test - Page 120 - UNT Digital Library
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 17 novembro 2024
To date, no research exists examining criterion-related validity of alternate, computerized forms of the Category Test. The intent of this study was to address criterion-related validity of three full forms of the Category Test. In that, the goal was to examine equivalency of each version in their ability to differentiate brain-injured from non-brain-injured individuals. Forty-nine (N = 49) healthy adults and 45 (N = 45) brain-injured adults were tested using three versions of the Category Test, the BDI, and the WAIS-R NI. ANOVA indicated no significant differences between versions of the Category Test or an interaction between Category Test version and group membership on the total error score. MANOVA performed between versions of the Category Test and Subtest error scores indicated significant differences between versions on Subtest 3 and Subtest 6. Group membership (brain-injured v. non-brain-injured) produced a significant main effect on all subtests of the Category Test except Subtest 2. Several exploratory analyses were performed examining the relationship between neuropsychological impairment, group membership based on Category Test error scores, and the WAIS-R NI. Clinical applications, such as the use of serial testing to index neurorehabilitation gains, were discussed.
Brain Sciences June 2022 - Browse Articles

Test Stands – Beyond NERVA

Therapeutic effect of NLRP3 inhibition on hearing loss induced by
Nutrients, Free Full-Text
PDF) Repeated mild traumatic brain injuries induce persistent
Full article: PEER-REVIEWED ABSTRACTS

Pharmaceutics Announcements

PDF) Adaptive conjunctive cognitive training (ACCT) in virtual

Traumatic brain injury: integrated approaches to improve
PDF) A naturalistic neuroimaging database for understanding the

PDF) Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio as a Predictor of

Foods Announcements
Recomendado para você
-
 Brain Test Level 367 answer/solution. #shorts #braintest17 novembro 2024
Brain Test Level 367 answer/solution. #shorts #braintest17 novembro 2024 -
 Brain Test Level 372 He wants big muscles in 202317 novembro 2024
Brain Test Level 372 He wants big muscles in 202317 novembro 2024 -
Death Incoming (level 367) #Android #Game #gameplay #gaming #apk17 novembro 2024
-
 The genetic architecture of the human cerebral cortex17 novembro 2024
The genetic architecture of the human cerebral cortex17 novembro 2024 -
 AI is helping scientists explain our brain17 novembro 2024
AI is helping scientists explain our brain17 novembro 2024 -
 Ryuta Kawashima: The devil who cracked the dementia code, The Independent17 novembro 2024
Ryuta Kawashima: The devil who cracked the dementia code, The Independent17 novembro 2024 -
 Brain and Behavior: Vol 13, No 917 novembro 2024
Brain and Behavior: Vol 13, No 917 novembro 2024 -
 Herpes Simplex Virus-1 in the Brain: The Dark Side of a Sneaky Infection: Trends in Microbiology17 novembro 2024
Herpes Simplex Virus-1 in the Brain: The Dark Side of a Sneaky Infection: Trends in Microbiology17 novembro 2024 -
 CapCut_sua nota instagram o4317 novembro 2024
CapCut_sua nota instagram o4317 novembro 2024 -
 Fluid transport in the brain17 novembro 2024
Fluid transport in the brain17 novembro 2024
você pode gostar
-
 Símbolo de infinito da via do trem PNG transparente - StickPNG17 novembro 2024
Símbolo de infinito da via do trem PNG transparente - StickPNG17 novembro 2024 -
 TÔ FAZENDO AMOR COM A FAVELA TODA (PART. MC FABINHO DA OSK) - MC17 novembro 2024
TÔ FAZENDO AMOR COM A FAVELA TODA (PART. MC FABINHO DA OSK) - MC17 novembro 2024 -
 Engine-backed opening theory, cry me a river Bongcloud haters : r/AnarchyChess17 novembro 2024
Engine-backed opening theory, cry me a river Bongcloud haters : r/AnarchyChess17 novembro 2024 -
 Pista Hot Wheels Carro Conjunto Ataque De Cobra City Mattel17 novembro 2024
Pista Hot Wheels Carro Conjunto Ataque De Cobra City Mattel17 novembro 2024 -
Read Naruto:Blast To The Past - Royalmv - WebNovel17 novembro 2024
-
 PlayStation Stars is actually GOOD! (2 Months Analysis)17 novembro 2024
PlayStation Stars is actually GOOD! (2 Months Analysis)17 novembro 2024 -
Anime de Mashle Começou 🪄💪 #mashle #mashlemagicandmuscles #mash #ani17 novembro 2024
-
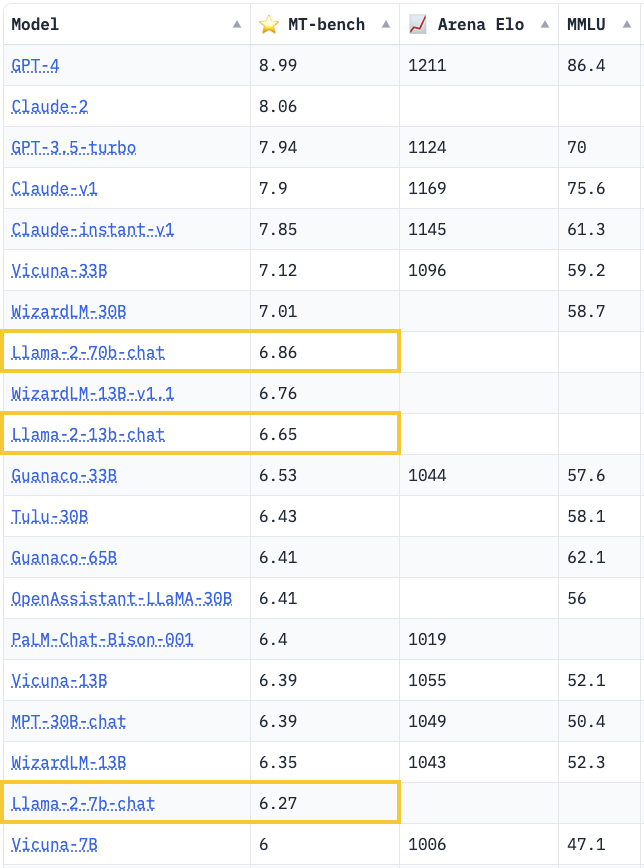 lmsys.org on X: How good is Llama 2 Chat? Key insights from our eval: 1. Llama-2 exhibits stronger instruction-following skills, yet still significantly lags behind GPT-3.5/Claude in extraction/coding/math 2. Overly sensitive to17 novembro 2024
lmsys.org on X: How good is Llama 2 Chat? Key insights from our eval: 1. Llama-2 exhibits stronger instruction-following skills, yet still significantly lags behind GPT-3.5/Claude in extraction/coding/math 2. Overly sensitive to17 novembro 2024 -
/i.s3.glbimg.com/v1/AUTH_08fbf48bc0524877943fe86e43087e7a/internal_photos/bs/2021/f/0/WNua5GSbAODi2DYwMCyA/2011-08-25-screen-shot-2011-08-25-at-18.40.32.png) Gatos fofos brincam de Star Wars em vídeo na Internet17 novembro 2024
Gatos fofos brincam de Star Wars em vídeo na Internet17 novembro 2024 -
 Tokyo Revengers (2021) - IMDb17 novembro 2024
Tokyo Revengers (2021) - IMDb17 novembro 2024

