Female-biased introductions produce higher predicted population size and genetic diversity in simulations of a small, isolated tiger (Panthera tigris) population
Por um escritor misterioso
Last updated 03 março 2025

Loop Samuel A Cushman

Non-Invasive Genotyping of Sumatran Elephants: Implications for
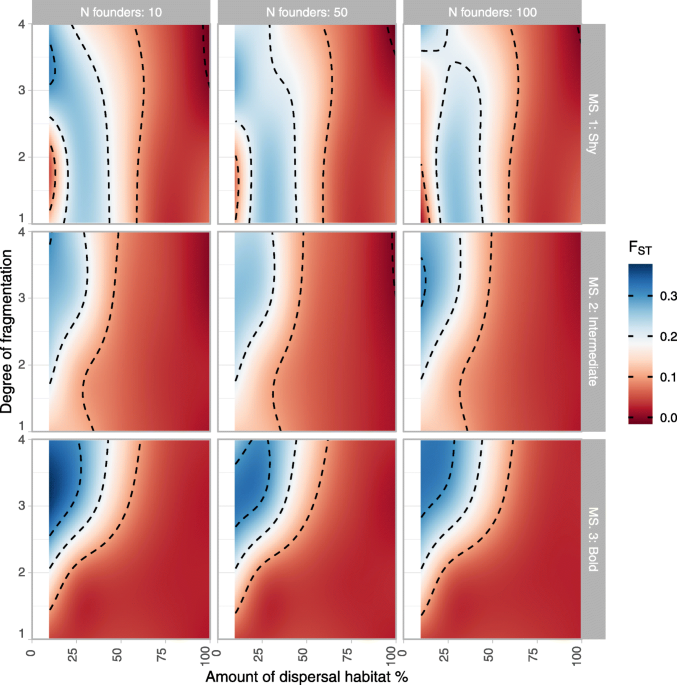
The boon and bane of boldness: movement syndrome as saviour
Fine-scale population genetic structure of the Bengal tiger
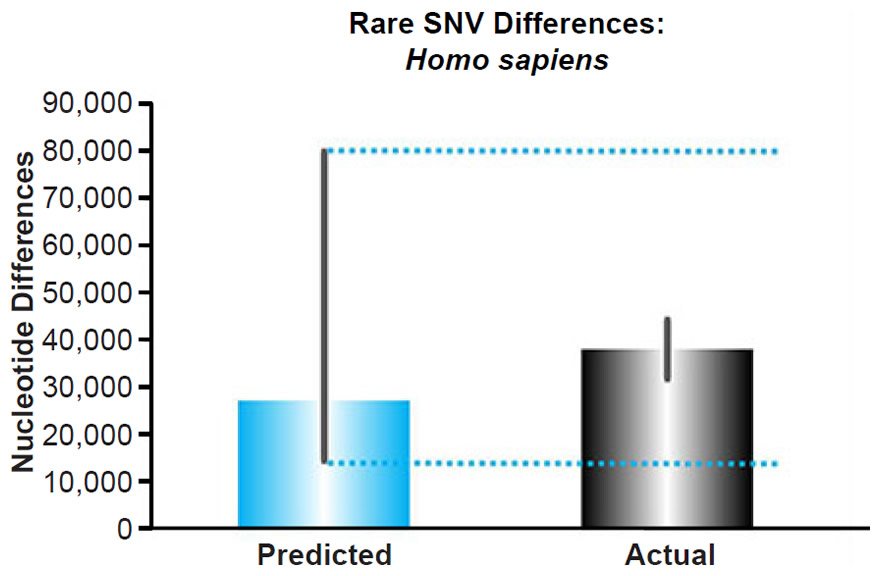
Origin Eukaryotic Genotypic Phenotypic Diversity

Origin Eukaryotic Genotypic Phenotypic Diversity

Non-Invasive Genotyping of Sumatran Elephants: Implications for

Demographic Stochasticity and Social Mating System in the Process
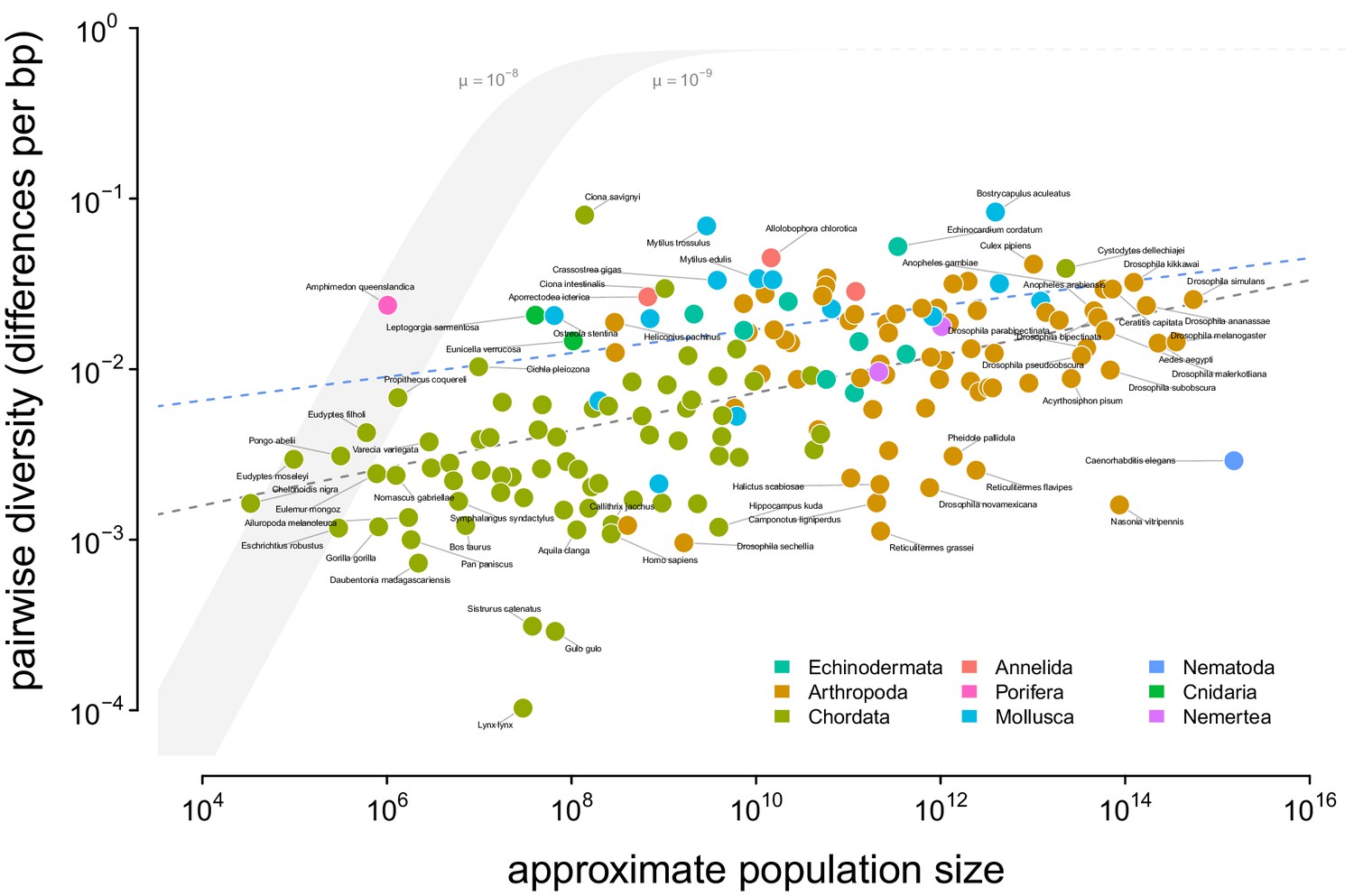
Quantifying the relationship between genetic diversity and

Wildlife Conservation Research Unit

Research Committee Newsletter 11 Issue, September 2008
Recomendado para você
-
 Bengal tiger - Wikipedia03 março 2025
Bengal tiger - Wikipedia03 março 2025 -
 Siberian tiger - Wikipedia03 março 2025
Siberian tiger - Wikipedia03 março 2025 -
 Ngandong Tiger, Dinopedia03 março 2025
Ngandong Tiger, Dinopedia03 março 2025 -
 Guangdong tigers hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy03 março 2025
Guangdong tigers hi-res stock photography and images - Alamy03 março 2025 -
 The genetics of tiger pelage color variations03 março 2025
The genetics of tiger pelage color variations03 março 2025 -
 7th Global Tiger Day03 março 2025
7th Global Tiger Day03 março 2025 -
 Southeast Asia Losing Tigers as Deadline Looms to Double Population by 202203 março 2025
Southeast Asia Losing Tigers as Deadline Looms to Double Population by 202203 março 2025 -
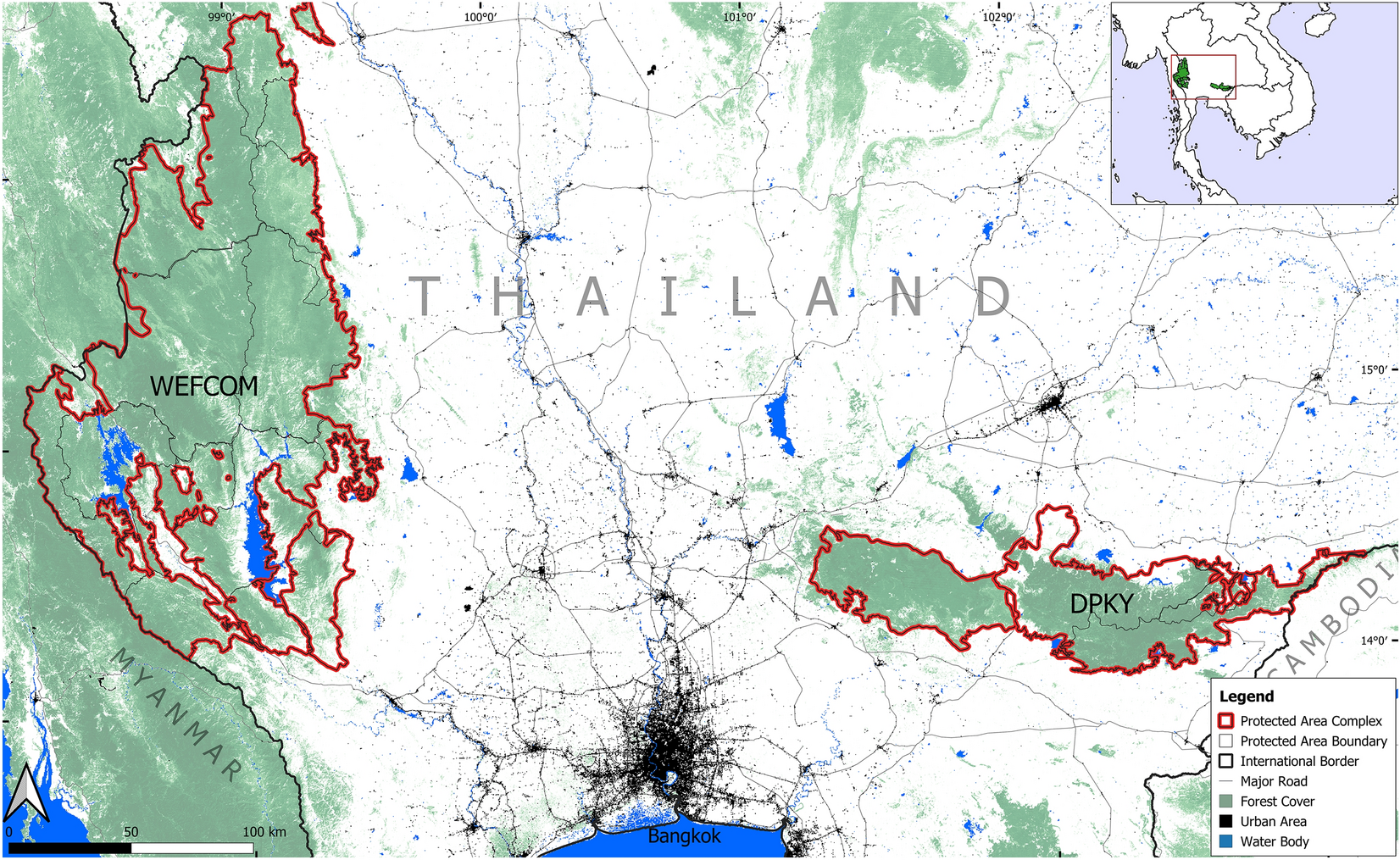
 Habitat connectivity for endangered Indochinese tigers in Thailand - ScienceDirect03 março 2025
Habitat connectivity for endangered Indochinese tigers in Thailand - ScienceDirect03 março 2025 -
 Six Notorious Tiger Poachers Have Been Caught in the Act — Species Unite03 março 2025
Six Notorious Tiger Poachers Have Been Caught in the Act — Species Unite03 março 2025 -
 Hawaiian Shirt Bob Dong, Hundred Tiger Aloha, Hawaiian Shirt Men03 março 2025
Hawaiian Shirt Bob Dong, Hundred Tiger Aloha, Hawaiian Shirt Men03 março 2025
você pode gostar
-
 How Much Internet Speed Do You Need for PS5?03 março 2025
How Much Internet Speed Do You Need for PS5?03 março 2025 -
The 20+ Best Anime Like KonoSuba03 março 2025
-
:quality(75)/arc-anglerfish-arc2-prod-elcomercio.s3.amazonaws.com/public/MD5GREDSABHSNA6AVBHW357S74.jpg) Pokémon GO: los Pokémon de tipo siniestro que hay en el juego, Viral, Truco, Tutorial, Smartphone, NNDA, NNRT, DATA03 março 2025
Pokémon GO: los Pokémon de tipo siniestro que hay en el juego, Viral, Truco, Tutorial, Smartphone, NNDA, NNRT, DATA03 março 2025 -
 Reddit - Dive into anything03 março 2025
Reddit - Dive into anything03 março 2025 -
![Deadpool - Parte 1: Eu Quero o Meu PRÓPRIO JOGO [ Playthrough Comentado em PT-BR ]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/CxY-jMiVSWE/maxresdefault.jpg) Deadpool - Parte 1: Eu Quero o Meu PRÓPRIO JOGO [ Playthrough Comentado em PT-BR ]03 março 2025
Deadpool - Parte 1: Eu Quero o Meu PRÓPRIO JOGO [ Playthrough Comentado em PT-BR ]03 março 2025 -
 Heart-Shaped Box: A Novel (English Edition) - eBooks em Inglês na03 março 2025
Heart-Shaped Box: A Novel (English Edition) - eBooks em Inglês na03 março 2025 -
 Post by Khe_Te_ImPoRtA in Gacha Cute Pc comments03 março 2025
Post by Khe_Te_ImPoRtA in Gacha Cute Pc comments03 março 2025 -
 The Maze Runner (2014) - MobyGames03 março 2025
The Maze Runner (2014) - MobyGames03 março 2025 -
 If only they knew >:) : r/roblox03 março 2025
If only they knew >:) : r/roblox03 março 2025 -
 The Pawn's Revenge Ch.44 Page 39 - Mangago03 março 2025
The Pawn's Revenge Ch.44 Page 39 - Mangago03 março 2025
